Mechanism of interleukin-1α transcriptional regulation of S100A9 in a human epidermal keratinocyte cell line
- PMID: 23563247
- PMCID: PMC3719387
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.03.010
Mechanism of interleukin-1α transcriptional regulation of S100A9 in a human epidermal keratinocyte cell line
Abstract
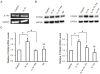
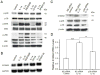
S100A9 is a calcium-binding protein and subunit of antimicrobial calprotectin complex (S100A8/A9). Produced by neutrophils, monocytes/macrophages and keratinocytes, S100A9 expression increases in response to inflammation. For example, IL-1α produced by epithelial cells acts autonomously on the same cells to induce the expression of S100A8/A9 and cellular differentiation. Whereas it is well known that IL-1α and members of the IL-10 family of cytokines upregulate S100A8 and S100A9 in several cell lineages, the pathway and mechanism of IL-1α-dependent transcriptional control of S100A9 in epithelial cells are not established. Modeled using human epidermal keratinocytes (HaCaT cells), IL-1α stimulated the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and induced S100A9 expression, which was blocked by IL-1 receptor antagonist, RNAi suppression of p38, or a p38 MAPK inhibitor. Transcription of S100A9 in HaCaT cells depended on nucleotides -94 to -53 in the upstream promoter region, based upon the use of deletion constructs and luciferase reporter activity. Within the responsive promoter region, IL-1α increased the binding activity of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β (C/EBPβ). Mutated C/EBPβ binding sequences or C/EBPβ-specific siRNA inhibited the S100A9 transcriptional response. Hence, IL-1α is strongly suggested to increase S100A9 expression in a human epidermal keratinocyte cell line by signaling through the IL-1 receptor and p38 MAPK, increasing C/EBPβ-dependent transcriptional activity.
Keywords: C/EBPβ; ERK; IL-1 receptor; IL-1R1; IL-1α; JNK; Keratinocytes; S100A9; TLR5; Toll-like receptor 5; c-JUN N-terminal kinase; extracellular-regulated kinase; p38; p38 kinase; siRNA; small interfering RNA.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Volz A, Korge BP, Compton JG, Ziegler A, Steinert PM, Mischke D. Physical mapping of a functional cluster of epidermal differentiation genes on chromosome 1q21. Genomics. 1993;18:92–99. - PubMed
-
- Fagerhol MK, Andersson KB, Naess-Andresen CF, Brandtzaeg P, Dale I. Calprotectin (The L1 leukocyte protein) In: Smith VL, Dedman JR, editors. Stimulus response coupling The role of intracellular calcium-binding proteins. CRC Press; Boca Raton, Ann Arbor, Boston, MA: 1990. pp. 187–210.
-
- Eversole LR, Miyasaki KT, Christensen RE. The distribution of the antimicrobial protein, calprotectin, in normal oral keratinocytes. Arch Oral Biol. 1992;37:963–968. - PubMed
-
- Kerkhoff C, Klempt M, Sorg C. Novel insights into structure and function of MRP8 (S100A8) and MRP14 (S100A9) Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1448:200–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

