CCDC22 deficiency in humans blunts activation of proinflammatory NF-κB signaling
- PMID: 23563313
- PMCID: PMC3635737
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI66466
CCDC22 deficiency in humans blunts activation of proinflammatory NF-κB signaling
Abstract
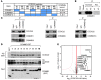
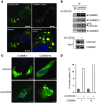
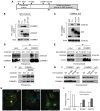
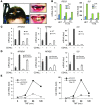
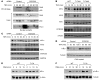
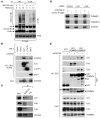
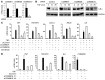
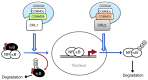
NF-κB is a master regulator of inflammation and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of immune disorders and cancer. Its regulation involves a variety of steps, including the controlled degradation of inhibitory IκB proteins. In addition, the inactivation of DNA-bound NF-κB is essential for its regulation. This step requires a factor known as copper metabolism Murr1 domain-containing 1 (COMMD1), the prototype member of a conserved gene family. While COMMD proteins have been linked to the ubiquitination pathway, little else is known about other family members. Here we demonstrate that all COMMD proteins bind to CCDC22, a factor recently implicated in X-linked intellectual disability (XLID). We showed that an XLID-associated CCDC22 mutation decreased CCDC22 protein expression and impaired its binding to COMMD proteins. Moreover, some affected individuals displayed ectodermal dysplasia, a congenital condition that can result from developmental NF-κB blockade. Indeed, patient-derived cells demonstrated impaired NF-κB activation due to decreased IκB ubiquitination and degradation. In addition, we found that COMMD8 acted in conjunction with CCDC22 to direct the degradation of IκB proteins. Taken together, our results indicate that CCDC22 participates in NF-κB activation and that its deficiency leads to decreased IκB turnover in humans, highlighting an important regulatory component of this pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of COMMD protein-protein interactions in NF-kappaB signalling.Biochem J. 2006 Aug 15;398(1):63-71. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051664. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16573520 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-associated domain-containing ubiquitin regulatory X (UBX) protein UBXN1 is a negative regulator of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 17;290(16):10395-405. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.631689. Epub 2015 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25681446 Free PMC article.
-
The COMMD Family Regulates Plasma LDL Levels and Attenuates Atherosclerosis Through Stabilizing the CCC Complex in Endosomal LDLR Trafficking.Circ Res. 2018 Jun 8;122(12):1648-1660. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.312004. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Circ Res. 2018. PMID: 29545368
-
Tuning NF-κB activity: a touch of COMMD proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1832(12):2315-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.09.014. Epub 2013 Sep 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24080195 Review.
-
Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity.Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:621-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.621. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10837071 Review.
Cited by
-
COMMD proteins function and their regulating roles in tumors.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 23;13:1067234. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1067234. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36776284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a novel CCDC22 mutation in a patient with severe Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and aggressive natural killer cell leukemia.Int J Hematol. 2019 Jun;109(6):744-750. doi: 10.1007/s12185-019-02595-0. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Int J Hematol. 2019. PMID: 30706328
-
Structural insights into the architecture and membrane interactions of the conserved COMMD proteins.Elife. 2018 Aug 1;7:e35898. doi: 10.7554/eLife.35898. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30067224 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Sex Differences in Autoimmune Diseases: Immunologic Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 23;26(15):7101. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157101. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural organization of the retriever-CCC endosomal recycling complex.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Jun;31(6):910-924. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01184-4. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38062209 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

