Effect of maternal undernutrition on human foetal pancreas morphology in second trimester of pregnancy
- PMID: 23563373
- PMCID: PMC3657853
Effect of maternal undernutrition on human foetal pancreas morphology in second trimester of pregnancy
Abstract
Background & objectives: Maternal undernutrition and hyperglycaemia during pregnancy, as well as foetal undernutrition affecting the development of foetal endocrine pancreas structure and function, especially that of β-cells is well known. This study was undertaken to look into the changes in pancreatic islets morphology of aborted normal human foetuses (16-20 wk old) of undernourished and adequately nourished mothers.
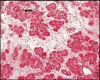
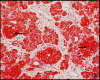
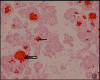
Methods: Foetuses were collected over a 24 month period from medically terminated pregnancies of six undernourished mothers (BMI <18.5 kg/m² and eight adequately nourished mothers (BMI >18.5 kg/m². The sections were stained with haematoxylin & eosin as well as Masson trichrome for morphometric estimates such as islet count, area, volume, etc. and immunohistochemistry analysis of β-cells for insulin presence was done.
Results: Significant correlations between maternal and foetal parameters were seen. However, there were no statistically significant differences in the number, size or density and beta cell counts of the pancreas among foetal pancreas of mothers with BMI <18.5 and >18.5 kg/m².
Interpretation & conclusions: Our findings indicate that nutritional status of the mother may not have profound influence on the morphology of beta cells of foetal pancreas in second trimester of pregnancy. Further studies need to be done to confirm these findings.
Figures
Comment in
-
Maternal nutrition, nutrient transfer & foetal pancreas development.Indian J Med Res. 2013 Feb;137(2):249-50. Indian J Med Res. 2013. PMID: 23563368 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Breant B, Gesina E, Blondeau B. Nutrition, gluco-corticoids and pancreas development. Horm Res. 2006;65(Suppl 3):98–104. Erratum in Horm Res 2006; 65 : 98-104. - PubMed
-
- Creve ME, Williams K, Nkomo XI, Muller CJ, Du Toit DF, Louw J, et al. Islet cell response in the neonatal rat after exposure to a high fat diet during pregnancy. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;288:1122–8. - PubMed
-
- Hales CN, Barker DJP. Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: the thrifty phenotype hypothesis. Diabetologia. 1992;35:595–601. - PubMed
-
- Wilson MR, Hughes SJ. The effect of maternal protein deficiency during pregnancy and lactation on glucose tolerance and pancreatic islet function in adult rat offspring. J Endocrinol. 1997;154:177–85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
