The role of urinary fractionated metanephrines in the diagnosis of phaeochromocytoma
- PMID: 23563375
- PMCID: PMC3657855
The role of urinary fractionated metanephrines in the diagnosis of phaeochromocytoma
Abstract
Background & objectives: Plasma and urinary metanephrines are used as screening tests for the diagnosis of phaeochromocytoma. The recommended cut-off levels are not standardized. This study was conducted to identify a cut-off level for 24 h urinary fractionated metanephrines viz. metanephrine (uMN) and normetanephrine (uNMN) using enzyme immunoassay for the diagnosis of phaeochromocytoma.
Methods: Consecutive patients suspected to have phaeochromocytoma were included in the study. uMN and uNMN in 24 h urinary sample were measured using a commercial ELISA kit.
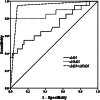
Results: Overall, 72 patients were included over a period of 18 months. Twenty patients had histopathologically confirmed phaeochromocytoma and in 52 patients phaeochromocytoma was ruled out. Using the upper limit of normal stated by the assay manufacturer as the cut-off, uMN >350 μg/day had a low sensitivity and uNMN >600 μg/day had a poor specificity. By increasing the cut-off value of uNMN to twice the upper limit, specificity increased significantly without much loss in sensitivity. Combining uMN and uNMN using a cut-off twice the upper limit improved the diagnostic performance - sensitivity (95%); specificity (92.3%); positive predictive value (PPV - 82.6%); negative predictive value (NPV - 98%). In subsets of patients with a variable pretest probability for phaeochromocytoma, the PPV correlates well with the occurred of these tumors decreased, while the NPV remained at 100 per cent.
Interpretation & conclusions: ELISA is a simple and reliable method for measuring uMN and uNMN. The test has a good NPV and can be used as an initial screening test for ruling out phaeochromocytoma. Each hospital will have to define the cut-off value for the assay being used, choosing a proper control population.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Correlation between urinary fractionated metanephrines in 24-hour and spot urine samples for evaluating the therapeutic effect of metyrosine: a subanalysis of a multicenter, open-label phase I/II study.Endocr J. 2019 Dec 25;66(12):1063-1072. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ19-0125. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Endocr J. 2019. PMID: 31511435 Clinical Trial.
-
Different diagnostic cut-off values of urinary fractionated metanephrines according to sex for the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma in Korean subjects.Endocr J. 2012;59(9):831-8. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.ej12-0052. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Endocr J. 2012. PMID: 22785075
-
Enzyme-linked immunoassay for plasma-free metanephrines in the biochemical diagnosis of phaeochromocytoma in adults is not ideal.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011 Oct 8;50(1):105-10. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2011.742. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011. PMID: 21981378
-
[Plasma metanephrine measurements make the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma easier].Lakartidningen. 1998 May 20;95(21):2482-5. Lakartidningen. 1998. PMID: 9640923 Review. Swedish.
-
[Metanephrine (M), normetanephrine (NM) and fractionated metanephrines].Nihon Rinsho. 2005 Aug;63 Suppl 8:395-8. Nihon Rinsho. 2005. PMID: 16149538 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Catecholamines and their O-methylated metabolites in vitreous humor in hypothermia cases.Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2016 Jun;12(2):163-9. doi: 10.1007/s12024-016-9764-2. Epub 2016 Mar 26. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27017494
-
Angiotensin II status and sympathetic activation among hypertensive patients in Uganda: a cross-sectional study.BMC Res Notes. 2015 Oct 20;8:586. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1544-7. BMC Res Notes. 2015. PMID: 26486596 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of recommended sampling and assay methods for the determination of plasma-free and urinary fractionated metanephrines in the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: a systematic review.Endocrine. 2017 Jun;56(3):495-503. doi: 10.1007/s12020-017-1300-y. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Endocrine. 2017. PMID: 28405881 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Urinary Metanephrines Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2891:257-268. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4334-1_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39812987
References
-
- Eisenhofer G, Lenders JW, Pacak K. Choice of biochemical test for diagnosis of pheochromocytoma: validation of plasma metanephrines. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2002;4:250–5. - PubMed
-
- Boyle JG, Davidson DF, Perry CG, Connell JM. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of urinary free metanephrines, vanillyl mandelic Acid, and catecholamines and plasma catecholamines for diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:4602–8. - PubMed
-
- Eisenhofer G, Huynh TT, Hiroi M, Pacak K. Understanding catecholamine metabolism as a guide to the biochemical diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2001;2:297–311. - PubMed
-
- Eisenhofer G. Free or total metanephrines for diagnosis of pheochromocytoma: what is the difference? Clin Chem. 2001;47:988–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
