Strategy for identification & characterization of Bartonella henselae with conventional & molecular methods
- PMID: 23563383
- PMCID: PMC3657863
Strategy for identification & characterization of Bartonella henselae with conventional & molecular methods
Abstract
Background & objectives: Bartonella henselae is a fastidious gram-negative bacterium usually causing self limiting infections in immunocompetent individuals but often causes potentially life threatening infection, such as bacillary angiomatosis in immunocompromised patients. Both diagnosis of infections and research into molecular mechanisms of pathogenesis have been hindered by lack of appropriate and reliable diagnostic techniques. We undertook this study to standardize methods to characterize B. henselae in clinical samples to diagnose Bartonella infection correctly.
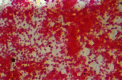
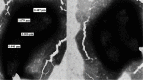
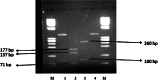
Methods: B. henselae ATCC 49882 strain was procured from American type culture collection, USA. This strain was revived and maintained in the laboratory, and identification and characterization of this strain was done by conventional and molecular techniques, which included culture on various media, staining by different methods including electron microscopy, biochemical analysis by conventional methods and API, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for amplification of citrate synthase gene followed by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP).
Results: This organism was biochemically inert due to slow growth and generated unique identification code with API. The amplification of the citrate-synthase gene with primers yielded a 381 bp product followed by specific RFLP profile for B. henselae.
Interpretation & conclusions: Bartonella is fastidious and fragile organism and should be handled carefully. Extra effort and careful observation are required to isolate and characterize this organism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bacillary angiomatosis in immunocompromised patients.AIDS. 1998 Oct 1;12(14):1793-803. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199814000-00011. AIDS. 1998. PMID: 9792380 Review.
-
Identification of Bartonella species directly in clinical specimens by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of a 16S rRNA gene fragment.J Clin Microbiol. 1999 Dec;37(12):4045-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.37.12.4045-4047.1999. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10565929 Free PMC article.
-
Strategy to detect and identify Bartonella species in routine clinical laboratory yields Bartonella henselae from human immunodeficiency virus-positive patient and unique Bartonella strain from his cat.J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Aug;33(8):2107-13. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.8.2107-2113.1995. J Clin Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 7559957 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of Bartonella-like isolates at the species level by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism in the citrate synthase gene.J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Jul;33(7):1797-803. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.7.1797-1803.1995. J Clin Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 7545181 Free PMC article.
-
[Bartonella henselae, an ubiquitous agent of proteiform zoonotic disease].Med Mal Infect. 2010 Jun;40(6):319-30. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2009.11.004. Epub 2009 Dec 29. Med Mal Infect. 2010. PMID: 20042306 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Blood Supplementation Enhances Bartonella henselae Growth and Molecular Detection of Bacterial DNA in Liquid Culture.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0512622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.05126-22. Epub 2023 May 25. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37227273 Free PMC article.
-
Biomolecular Investigation of Bartonella spp. in Wild Rodents of Two Swiss Regions.Pathogens. 2021 Oct 15;10(10):1331. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10101331. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34684280 Free PMC article.
-
Two novel Bartonella (sub)species isolated from edible dormice (Glis glis): hints of cultivation stress-induced genomic changes.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 15;14:1289671. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1289671. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38033559 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of Bartonella henselae infection in pet and stray cats in Croatia with risk factors analysis.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Feb 1;17(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06117-8. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38303085 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, characterization, and molecular identification of soil bacteria showing antibacterial activity against human pathogenic bacteria.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021 Aug 18;19(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s43141-021-00219-x. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34406527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anna Sander. Bartonella and Afipia. In: Collier L, Balows A, Sussman M, Duerden BI, editors. Topley & Wilson's microbiology and microbial infections. 9th ed. II. New York: Hodder Arnold; 1998. p. 133.
-
- Kaiser PO, Riess T, O’Rourke F, Linke D, Kempf VAJ. Bartonella spp.: throwing light on uncommon human infections. Int J Med Microbiol. 2011;301:7–15. - PubMed
-
- Higgins JA, Radulovic S, Jaworski DC, Azad AF. Acquisition of the cat scratch disease agent Bartonella henselae by cat fleas (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) J Med Entomol. 1996;33:490–5. - PubMed
-
- Marié JL, Fournier PE, Rolain JM, Briolant S, Davoust B, Raoult D. Molecular detection of Bartonella quintana. B. Elizabethae, B. Koehlerae, B. Doshiae, B. Taylorii, and Rickettsia Felis in rodent fleas collected in Kabul, Afghanistan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006;74:436–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
