Theory, measurement and hard times: some issues for HIV/AIDS research
- PMID: 23564029
- PMCID: PMC3674169
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-013-0475-3
Theory, measurement and hard times: some issues for HIV/AIDS research
Abstract
Economic and political instability and related "big events" are widespread throughout the globe. Although they sometimes lead to epidemic HIV outbreaks, sometimes they do not-and we do not understand why. Current behavioural theories do not adequately address these processes, and thus cannot provide optimal guidance for effective intervention. Based in part on a critique of our prior "pathways" model of big events, we suggest that cultural-historical activity theory (CHAT) may provide a useful framework for HIV research in this area. Using CHAT concepts, we also suggest a number of areas in which new measures should be developed to make such research possible.
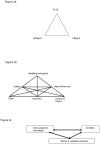
Figures


References
-
- Kentikelenis A, Karanikolos M, Papanicolas I, Basu S, McKee M, Stuckler D. Health effects of financial crisis: Omens of a Greek tragedy. Lancet. 2011 - PubMed
-
- Pharris A, Wiessing L, Sfetcu O, Hedrich D, Botescu A, Fotiou A, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus in injecting drug users in Europe following a reported increase of cases in Greece and Romania, 2011. Euro surveillance. 2011;16(48) - PubMed
-
- Paraskevis D, Nikolopoulos G, Tsiara C, Paraskeva D, Antoniadou A, Lazanas M, et al. HIV-1 outbreak among injecting drug users in Greece, 2011: a preliminary report. Euro surveillance: bulletin europeen sur les maladies transmissibles. European communicable disease bulletin. 2011;16(36) - PubMed
-
- Brudney K, Dobkin J. Resugent tuberculosis in New York City: Human Immunodeficiency virus, homelessness, and the decline of tuberculosis control programs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991;144:745–747. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

