Minimal interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor stalk composition for IL-6 receptor shedding and IL-6 classic signaling
- PMID: 23564454
- PMCID: PMC3663500
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.466169
Minimal interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor stalk composition for IL-6 receptor shedding and IL-6 classic signaling
Abstract
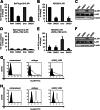
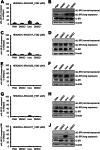
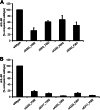
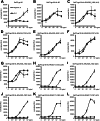
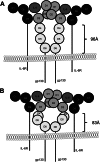
Signaling of the pleiotropic cytokine Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is coordinated by membrane-bound and soluble forms of the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) in processes called classic and trans-signaling, respectively. The soluble IL-6R is mainly generated by ADAM10- and ADAM17-mediated ectodomain shedding. Little is known about the role of the 52-amino acid-residue-long IL-6R stalk region in shedding and signal transduction. Therefore, we generated and analyzed IL-6R stalk region deletion variants for cleavability and biological activity. Deletion of 10 amino acids of the stalk region surrounding the ADAM17 cleavage site substantially blocked IL-6R proteolysis by ADAM17 but only slightly affected proteolysis by ADAM10. Interestingly, additional deletion of the remaining five juxtamembrane-located amino acids also abrogated ADAM10-mediated IL-6R shedding. Larger deletions within the stalk region, that do not necessarily include the ADAM17 cleavage site, also reduced ADAM10 and ADAM17-mediated IL-6R shedding, questioning the importance of cleavage site recognition. Furthermore, we show that a 22-amino acid-long stalk region is minimally required for IL-6 classic signaling. The gp130 cytokine binding sites are separated from the plasma membrane by ~96 Å. 22 amino acid residues, however, span maximally 83.6 Å (3.8 Å/amino acid), indicating that the three juxtamembrane fibronectin domains of gp130 are not necessarily elongated but somehow flexed to allow IL-6 classic signaling. Our findings underline a dual role of the IL-6R stalk region in IL-6 signaling. In IL-6 trans-signaling, it regulates proper proteolysis by ADAM10 and ADAM17. In IL-6 classic-signaling, it acts as a spacer to ensure IL-6·IL-6R·gp130 signal complex formation.
Keywords: ADAM ADAMTS; ADAM10; ADAM17; IL-6 Signal Transduction; Interleukin; Interleukin-6; Interleukin-6 Receptor; Proteolytic Enzymes; Receptor Structure-Function; Signal Transduction.
Figures


References
-
- Scheller J., Chalaris A., Schmidt-Arras D., Rose-John S. (2011) The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1813, 878–888 - PubMed
-
- Garbers C., Hermanns H. M., Schaper F., Müller-Newen G., Grötzinger J., Rose-John S., Scheller J. (2012) Plasticity and cross-talk of interleukin 6-type cytokines. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 23, 85–97 - PubMed
-
- Sprecher C. A., Grant F. J., Baumgartner J. W., Presnell S. R., Schrader S. K., Yamagiwa T., Whitmore T. E., O'Hara P. J., Foster D. F. (1998) Cloning and characterization of a novel class I cytokine receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 246, 82–90 - PubMed
-
- Boulanger M. J., Chow D. C., Brevnova E. E., Garcia K. C. (2003) Hexameric structure and assembly of the interleukin-6/IL-6 α-receptor/gp130 complex. Science 300, 2101–2104 - PubMed
-
- Jostock T., Müllberg J., Ozbek S., Atreya R., Blinn G., Voltz N., Fischer M., Neurath M. F., Rose-John S. (2001) Soluble gp130 is the natural inhibitor of soluble interleukin-6 receptor transsignaling responses. Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 160–167 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

