Characterization of European ancestry nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-associated variants in individuals of African and Hispanic descent
- PMID: 23564467
- PMCID: PMC3782998
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.26440
Characterization of European ancestry nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-associated variants in individuals of African and Hispanic descent
Abstract
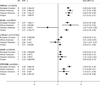
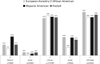
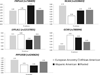
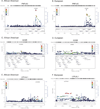
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is an obesity-related condition affecting over 50% of individuals in some populations and is expected to become the number one cause of liver disease worldwide by 2020. Common, robustly associated genetic variants in/near five genes were identified for hepatic steatosis, a quantifiable component of NAFLD, in European ancestry individuals. Here we tested whether these variants were associated with hepatic steatosis in African- and/or Hispanic-Americans and fine-mapped the observed association signals. We measured hepatic steatosis using computed tomography in five African American (n = 3,124) and one Hispanic American (n = 849) cohorts. All analyses controlled for variation in age, age(2) , gender, alcoholic drinks, and population substructure. Heritability of hepatic steatosis was estimated in three cohorts. Variants in/near PNPLA3, NCAN, LYPLAL1, GCKR, and PPP1R3B were tested for association with hepatic steatosis using a regression framework in each cohort and meta-analyzed. Fine-mapping across African American cohorts was conducted using meta-analysis. African- and Hispanic-American cohorts were 33.9/37.5% male, with average age of 58.6/42.6 years and body mass index of 31.8/28.9 kg/m(2) , respectively. Hepatic steatosis was 0.20-0.34 heritable in African- and Hispanic-American families (P < 0.02 in each cohort). Variants in or near PNPLA3, NCAN, GCKR, PPP1R3B in African Americans and PNPLA3 and PPP1R3B in Hispanic Americans were significantly associated with hepatic steatosis; however, allele frequency and effect size varied across ancestries. Fine-mapping in African Americans highlighted missense variants at PNPLA3 and GCKR and redefined the association region at LYPLAL1.
Conclusion: Multiple genetic variants are associated with hepatic steatosis across ancestries. This explains a substantial proportion of the genetic predisposition in African- and Hispanic-Americans. Missense variants in PNPLA3 and GCKR are likely functional across multiple ancestries.
© 2013 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Bellentani S, Marino M. Epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) Ann Hepatol. 2009;8(Suppl 1):S4–S8. - PubMed
-
- Harrison SA, Neuschwander-Tetri BA. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Liver Dis. 2004;8:861–879. ix. - PubMed
-
- Stepanova M, Younossi ZM. Independent Association Between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Cardiovascular Disease in the US Population. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10:646–650. - PubMed
-
- Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J, Sanderson SO, Lindor KD, Feldstein A, Angulo P. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:113–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 DK080145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL061210/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095170/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK081350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087660/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095172/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072488/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL060894/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087700/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL060944/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095171/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 HL100245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL061019/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL060919/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085571/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
