In vitro toxicological characterization of two arsenosugars and their metabolites
- PMID: 23564523
- PMCID: PMC3739928
- DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.201200821
In vitro toxicological characterization of two arsenosugars and their metabolites
Abstract
Scope: In their recently published Scientific Opinion on Arsenic in Food, the European Food Safety Authority concluded that a risk assessment for arsenosugars is currently not possible, largely because of the lack of relevant toxicological data. To address this issue, we carried out a toxicological in vitro characterization of two arsenosugars and six arsenosugar metabolites.
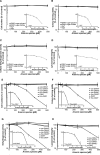
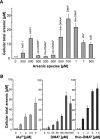
Methods and results: The highly pure synthesized arsenosugars, DMA(V) -sugar-glycerol and DMA(V) -sugar-sulfate, investigated in this study, as well as four metabolites, oxo-dimethylarsenoacetic acid (oxo-DMAA(V) ), oxo-dimethylarsenoethanol (oxo-DMAE(V) ), thio-DMAA(V) and thio-DMAE(V) , exerted neither cytotoxicity nor genotoxicity up to 500 μM exposure in cultured human bladder cells. However, two arsenosugar metabolites, namely dimethyl-arsinic acid (DMA(V) ) and thio-dimethylarsinic acid (thio-DMA(V) ), were toxic to the cells; thio-DMA(V) was even slightly more cytotoxic than arsenite. Additionally, intestinal bioavailability of the arsenosugars was assessed applying the Caco-2 intestinal barrier model. The observed low, but significant transfer rates of the arsenosugars across the barrier model provide further evidence that arsenosugars are intestinally bioavailable.
Conclusion: In a cellular system that metabolizes arsenosugars, cellular toxicity likely arises. Thus, in strong contrast to arsenobetaine, arsenosugars cannot be categorized as nontoxic for humans and a risk to human health cannot be excluded.
Keywords: Arsenosugars; Cellular and intestinal bioavailability; Cellular toxicity; Genotoxicity; Marine food.
© 2013 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vitro intestinal bioavailability of arsenosugar metabolites and presystemic metabolism of thio-dimethylarsinic acid in Caco-2 cells.Metallomics. 2013 Aug;5(8):1031-42. doi: 10.1039/c3mt00039g. Metallomics. 2013. PMID: 23752250 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicological properties of the thiolated inorganic arsenic and arsenosugar metabolite thio-dimethylarsinic acid in human bladder cells.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2014 Apr;28(2):138-146. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jul 5. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 23994116
-
Toxicological characterisation of a thio-arsenosugar-glycerol in human cells.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2016 Dec;38:150-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2016.04.013. Epub 2016 Apr 30. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27160015
-
Thiolated arsenicals in arsenic metabolism: Occurrence, formation, and biological implications.J Environ Sci (China). 2016 Nov;49:59-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2016.08.016. Epub 2016 Oct 7. J Environ Sci (China). 2016. PMID: 28007180 Review.
-
Analytical methods for the determination of arsenosugars--a review of recent trends and developments.Anal Chim Acta. 2010 Jan 11;657(2):83-99. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.10.041. Anal Chim Acta. 2010. PMID: 20005319 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis and Risk Assessment of Seaweed.EFSA J. 2019 Sep 17;17(Suppl 2):e170915. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2019.e170915. eCollection 2019 Sep. EFSA J. 2019. PMID: 32626473 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic potential for arsenic efflux and methylation varies among global Prochlorococcus populations.ISME J. 2016 Jan;10(1):197-209. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.85. Epub 2015 Jul 7. ISME J. 2016. PMID: 26151644 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating a Two-Way Street: Metal Toxicity and the Human Gut Microbiome.Environ Health Perspect. 2022 Mar;130(3):32001. doi: 10.1289/EHP9731. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Environ Health Perspect. 2022. PMID: 35302387 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Concentrations and speciation of arsenic in New England seaweed species harvested for food and agriculture.Chemosphere. 2016 Nov;163:6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.004. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Chemosphere. 2016. PMID: 27517127 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of arsenic speciation on accumulation and toxicity of dietborne arsenic exposures to rainbow trout.Aquat Toxicol. 2019 May;210:227-241. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Aquat Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30877964 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Straif K, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Baan R, Grosse Y, et al. A review of human carcinogens–part C: Metals, arsenic, dusts, and fibres. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:453–454. - PubMed
-
- IARC. Lyon, France: 1987. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Supplement 7, Overall Evaluations of Carcinogenicity: An Updating of IARC Monographs Volumes 1 to 42.
-
- EFSA. Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAMEuropean Food Safety Authority (EFSAScientific Opinion on Arsenic in Food. EFSA J. 2009;7:1–198. 1351.
-
- WHO. WHO Technical Report Series; No. 959, World Health Organization 2011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

