Complement in immune and inflammatory disorders: therapeutic interventions
- PMID: 23564578
- PMCID: PMC3623010
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203200
Complement in immune and inflammatory disorders: therapeutic interventions
Abstract
With the awareness that immune-inflammatory cross-talk is at the heart of many disorders, the desire for novel immunomodulatory strategies in the therapy of such diseases has grown dramatically. As a prime initiator and important modulator of immunological and inflammatory processes, the complement system has emerged as an attractive target for early and upstream intervention in inflammatory diseases and has moved into the spotlight of drug discovery. Although prevalent conditions such as age-related macular degeneration have attracted the most attention, the diverse array of complement-mediated pathologies, with distinct underlying mechanisms, demands a multifaceted arsenal of therapeutic strategies. Fortunately, efforts in recent years have not only introduced the first complement inhibitors to the clinic but also filled the pipelines with promising candidates. With a focus on immunomodulatory strategies, in this review we discuss complement-directed therapeutic concepts and highlight promising candidate molecules.
Figures
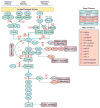
References
-
- Drews J. Paul Ehrlich: magister mundi. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:797–801. - PubMed
-
- Hussell T. Immune modulatory strategies: a playground with a swing and a seesaw. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012;10:249–251. - PubMed
-
- Zeerleder S. C1-inhibitor: more than a serine protease inhibitor. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2011;37:362–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI003040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DE021685/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- AI072106/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM097747/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI030040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM097747/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- EY020633/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE021685/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY020633/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- AI097805/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI068730/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI097805/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI068730/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI072106/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

