Adding once-daily lixisenatide for type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with newly initiated and continuously titrated basal insulin glargine: a 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled study (GetGoal-Duo 1)
- PMID: 23564915
- PMCID: PMC3747901
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-2462
Adding once-daily lixisenatide for type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with newly initiated and continuously titrated basal insulin glargine: a 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled study (GetGoal-Duo 1)
Abstract
Objective: When oral therapy for type 2 diabetes is ineffective, adding basal insulin improves glycemic control. However, when glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) remains elevated because of postprandial hyperglycemia, the next therapeutic step is controversial. We examined the efficacy and safety of lixisenatide in patients with HbA1c still elevated after initiation of insulin glargine.
Research design and methods: This double-blind, parallel-group trial enrolled patients with HbA1c 7-10% despite oral therapy. Insulin glargine was added and systematically titrated during a 12-week run-in, after which candidates with fasting glucose ≤ 7.8 mmol/L and HbA1c 7-9% were randomized to lixisenatide 20 µg or placebo for 24 weeks while insulin titration continued. The primary end point was HbA1c change after randomization.
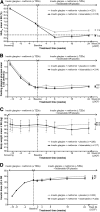
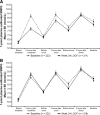
Results: The randomized population (n = 446) had mean diabetes duration of 9.2 years, BMI 31.8 kg/m(2), and daily glargine dosage of 44 units. HbA1c had decreased during run-in from 8.6 to 7.6%; adding lixisenatide further reduced HbA1c by 0.71 vs. 0.40% with placebo (least squares mean difference, -0.32%; 95% CI, -0.46 to -0.17; P < 0.0001). More participants attained HbA1c <7% with lixisenatide (56 vs. 39%; P < 0.0001). Lixisenatide reduced plasma glucose 2 h after a standardized breakfast (difference vs. placebo -3.2 mmol/L; P < 0.0001) and had a favorable effect on body weight (difference vs. placebo -0.89 kg; P = 0.0012). Nausea, vomiting, and symptomatic hypoglycemia <3.3 mmol/L were more common with lixisenatide.
Conclusions: Adding lixisenatide to insulin glargine improved overall and postprandial hyperglycemia and deserves consideration as an alternative to prandial insulin for patients not reaching HbA1c goals with recently initiated basal insulin.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00975286.
Figures
References
-
- Riddle MC. Timely initiation of basal insulin. Am J Med 2004;116(Suppl. 3A):3S–9S - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, et al. American Diabetes Association. European Association for the Study of Diabetes Medical management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetologia 2009;52:17–30 - PubMed
-
- Riddle MC, Rosenstock J, Gerich J, Insulin Glargine 4002 Study Investigators The treat-to-target trial: randomized addition of glargine or human NPH insulin to oral therapy of type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2003;26:3080–3086 - PubMed
-
- Raccah D, Bretzel RG, Owens D, Riddle M. When basal insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus is not enough—what next? Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2007;23:257–264 - PubMed
-
- Woerle HJ, Neumann C, Zschau S, et al. Impact of fasting and postprandial glycemia on overall glycemic control in type 2 diabetes Importance of postprandial glycemia to achieve target HbA1c levels. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2007;77:280–285 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

