Glucagon-like peptide 1 reduces endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and oxidative stress induced by both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 23564922
- PMCID: PMC3714509
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-2469
Glucagon-like peptide 1 reduces endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and oxidative stress induced by both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: Hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia currently are considered risk factors for cardiovascular disease in type 1 diabetes. Both acute hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia induce endothelial dysfunction and inflammation, raising the oxidative stress. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) has antioxidant properties, and evidence suggests that it protects endothelial function.
Research design and methods: The effect of both acute hyperglycemia and acute hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes, with or without the simultaneous infusion of GLP-1, on oxidative stress (plasma nitrotyrosine and plasma 8-iso prostaglandin F2alpha), inflammation (soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and interleukin-6), and endothelial dysfunction has been evaluated.
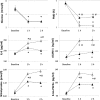
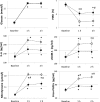
Results: Both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia acutely induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction. GLP-1 significantly counterbalanced these effects.
Conclusions: These results suggest a protective effect of GLP-1 during both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia in type 1 diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Wright RJ, Frier BM. Vascular disease and diabetes: is hypoglycaemia an aggravating factor? Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2008;24:353–363 - PubMed
-
- Singh P, Jain A, Kaur G. Impact of hypoglycemia and diabetes on CNS: correlation of mitochondrial oxidative stress with DNA damage. Mol Cell Biochem 2004;260:153–159 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

