Identification of QTLs associated with seedling root traits and their correlation with plant height in wheat
- PMID: 23564959
- PMCID: PMC3617839
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ert041
Identification of QTLs associated with seedling root traits and their correlation with plant height in wheat
Abstract
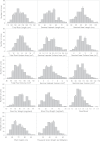
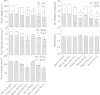
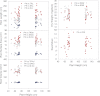
Genetic relationships between plant height and root morphology were investigated in a diverse set of wheat germplasm [199 double-haploid progeny derived from a cross between Avalon and Cadenza (Triticum aestivum L.), Rht near-isogenic lines (NILs), and accessions from the Watkins Collection] to investigate whether Rht genes controlling shoot height also control seedling root growth. A germination paper screen was developed to measure seedling root length (distinguishing seminal axes from seminal lateral roots), surface area, volume, and dry weight, and these were compared with shoot dry weight and the root to shoot ratio. Field experiments were conducted to measure mature plant height (PH) and grain characteristics for the mapping population. Forty-three quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for PH, root and seed traits were identified. Some QTLs for roots and either height or seed characteristics were coincident: chromosome 2D had co-locating root and PH QTLs; chromosomes 4D had co-locating root, PH, and seed QTLs; chromosome 5A and 6A had co-locating root and seed QTLs; and other non-co-locating root and PH QTLs were found on chromosomes 3A and 3B. Rht NILs illustrated that some known dwarfing genes reduce both PH and root proliferation. However, analysis of 25 short and 23 tall lines from the Watkins wheat germplasm collection indicated that PH and root proliferation are not simply related.
Figures

References
-
- Addisu M, Snape JW, Simmonds JR, Gooding MJ. 2009. Reduced height (Rht) and photoperiod insensitivity (Ppd) allele associations with establishment and early growth of wheat in contrasting production systems. Euphytica 166, 249–267
-
- Ahmed TA, Tsujimoto H, Sasakuma T. 2000. QTLs associated with plant height and related characters in haploid wheat. Breeding Science 50, 267–273
-
- Basten C, Weir BS, Zeng ZB. 1994. Zmap—a QTL cartographer. In: Smith C, Gavora JS, Benkel B, Chesnais J, Fairfull W, Gibson JP, Kennedy BW, Burnside EB, eds. Proceedings of the 5th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production: Computing Strategies and Software, Guelph, Organizing Committee; 22, 85–66
-
- Börner A, Röder M, Korzun V. 1997. Comparative molecular mapping of GA insensitive Rht loci on chromosomes 4B and 4D of common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics 95, 1133–1137
-
- Bremner PM, Eckersall RN, Scott RK. 1963. The relative importance of embryo size and endosperm size in causing the effects associated with seed size in wheat. Journal of Agricultural Science 61, 139–145
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

