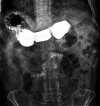
Megaduodenum in a patient with acromegaly
- PMID: 23565414
- PMCID: PMC3603062
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.104076
Megaduodenum in a patient with acromegaly
Abstract
Introduction: Acromegaly is associated with enlargement of all organs including the gastro intestinal system. However, there are no previous reports of occurrence of megaduodenum in patients with acromegaly.
Discussion: We present the case of a 47 year old male who was diagnosed to have acromegaly 13 years ago and had undergone transsphenoidal surgery twice with incomplete removal of the pituitary macro-adenoma and received radiotherapy following the second surgery. Patient has been on replacement therapy for hypocortisolism, hypothyroidism and hypogonadism since 10 years. Post glucose growth hormone level continued to remain unsuppressed; however, patient never received any medical therapy for acromegaly. He was evaluated with esophago-gastro-duodenoscopy for recurrent abdominal pain and distension, which showed an elongated and tortuous megaduodenum. These findings were verified with a barium study which revealed dilated stomach, first and second part of duodenum with no evidence of a distal obstruction.
Conclusions: We report this finding in view of the rare association.
Keywords: Acromegaly; duodenum; megaduodenum.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Baichi Matthew M, Arifuddin Razi M, Mantry Parvez S. Scleroderma Presenting as Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction. Pract Gastro Enterology. 2004
-
- Colemont LJ, Camilleri M. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: Diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 1989;64:60–70. - PubMed
-
- Baris D, Gridley G, Ron E, Weiderpass E, Mellemkjaer L, Ekbom A, et al. Acromegaly and cancer risk: A cohort study in Sweden and Denmark. Can Caus Cont. 2002;13:395–400. - PubMed
-
- Matano Y, Okada T, Suzuki A, Yoneda T, Takeda Y, Mabuchi H. Risk of colorectal neoplasm in patients with acromegaly and its relationship with serum growth hormone levels. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100:1154–60. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources