Correlation of CD44v6 expression with ovarian cancer progression and recurrence
- PMID: 23565736
- PMCID: PMC3635997
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-182
Correlation of CD44v6 expression with ovarian cancer progression and recurrence
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Correlation of CD44v6 expression with ovarian cancer progression and recurrence.BMC Cancer. 2020 Mar 19;20(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06753-0. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32192432 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Previously some groups demonstrated that CD44 variant 6 (CD44v6) is correlated with progression and metastasis of ovarian cancer. However, a number of other groups failed to find such an association. Moreover, epithelial ovarian cancer is known to easily metastasize to distinct sites such as the pelvic and abdominal cavities, but the potential association of CD44v6 expression with site-specific metastasis of ovarian cancer has not been explored. This study sought to evaluate the expression of CD44 standard (CD44s) and CD44v6 in primary, metastatic and recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer to explore the potential association of CD44s and CD44v6 with tumor progression and recurrence.
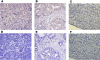
Methods: Tumor specimens were procured from patients with advanced (FIGO III, G3) and recurrent ovarian serous adenocarcinoma. CD44s and CD44v6 expression in the tumor tissues was evaluated by real-time RT-PCR and Western blot. Moreover, serum soluble CD44s or CD44v6 concentrations of early stage (FIGO I, G1), advanced (FIGO III, G3) and recurrent ovarian serous adenocarcinoma patients were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). CD44v6 expression in a different set of tumor samples on an ovarian cancer tissue chip was evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and the correlation of CD44v6 expression with clinicopathologic features was analyzed. Finally, the effects of knockdown of CD44v6 in SKOV3 cells on cell adhesion, invasion and migration were assessed.
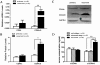
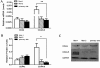
Results: The expression of CD44v6, but not CD44s, is up-regulated in recurrent ovarian serous cancer compared to advanced primary tumor. CD44v6 expression is also preferentially increased in the tumor at the abdominal cavity metastasis site of advanced diseases. Consistently, serum soluble CD44v6 levels of recurrent ovarian cancer were higher than those of early stage and advanced primary diseases. The IHC data demonstrate that CD44v6 expression is correlated with clinicopathologic features and tumor progression. Lastly, knockdown of CD44v6 decreases the adhesion and migration but not invasion capacities of SKOV3 cells.
Conclusions: CD44v6 expression levels are associated with epithelial ovarian cancer progression, metastasis and relapse. Moreover, serum soluble CD44v6 may be used as a potential marker for identifying tumor relapse. Finally, CD44v6 may play a role in ovarian cancer metastasis by mediating tumor cell adhesion and migration.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CD44 variant 6 is correlated with peritoneal dissemination and poor prognosis in patients with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer.Cancer Sci. 2015 Oct;106(10):1421-8. doi: 10.1111/cas.12765. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 26250934 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and significance of CD44s, CD44v6, and nm23 mRNA in human cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Nov 14;11(42):6601-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i42.6601. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16425351 Free PMC article.
-
CD44 standard form expression is correlated with high-grade and advanced-stage ovarian carcinoma but not prognosis.Hum Pathol. 2013 Sep;44(9):1882-9. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2013.02.016. Epub 2013 May 7. Hum Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23664487 Free PMC article.
-
CD44v6 engages in colorectal cancer progression.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jan 10;10(1):30. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1265-7. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30631039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cd44v6 acts as a directional responding factor in the process of transcoelomic metastasis from gastric carcinoma to Krukenberg tumor.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2023 Jul-Dec;23(7):583-588. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2023.2223981. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2023. PMID: 37409376 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of Specific CD44 Isoforms Is Associated with Aggressive Cell Features in Acquired Endocrine Resistance.Front Oncol. 2016 Jun 20;6:145. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00145. eCollection 2016. Front Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27379207 Free PMC article.
-
CD44v/CD44s expression patterns are associated with the survival of pancreatic carcinoma patients.Diagn Pathol. 2014 Apr 8;9:79. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-9-79. Diagn Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24708709 Free PMC article.
-
CD44 variant 6 is correlated with peritoneal dissemination and poor prognosis in patients with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer.Cancer Sci. 2015 Oct;106(10):1421-8. doi: 10.1111/cas.12765. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 26250934 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of CD44v6 expression in gastric carcinoma by the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway and its clinical significance.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 11;8(28):45848-45861. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17435. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28507278 Free PMC article.
-
Retraction Note: Correlation of CD44v6 expression with ovarian cancer progression and recurrence.BMC Cancer. 2020 Mar 19;20(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06753-0. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32192432 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

