Intra-membrane signaling between the voltage-gated Ca2+-channel and cysteine residues of syntaxin 1A coordinates synchronous release
- PMID: 23567899
- PMCID: PMC3621091
- DOI: 10.1038/srep01620
Intra-membrane signaling between the voltage-gated Ca2+-channel and cysteine residues of syntaxin 1A coordinates synchronous release
Abstract
The interaction of syntaxin 1A (Sx1A) with voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC) is required for depolarization-evoked release. However, it is unclear how the signal is transferred from the channel to the exocytotic machinery and whether assembly of Sx1A and the calcium channel is conformationally linked to triggering synchronous release. Here we demonstrate that depolarization-evoked catecholamine release was decreased in chromaffin cells infected with semliki forest viral vectors encoding Sx1A mutants, Sx1A(C271V), or Sx1A(C272V), or by direct oxidation of these Sx1A transmembrane (TM) cysteine residues. Mutating or oxidizing these highly conserved Sx1A Cys271 and Cys272 equally disrupted the Sx1A interaction with the channel. The results highlight the functional link between the VGCC and the exocytotic machinery, and attribute the redox sensitivity of the release process to the Sx1A TM C271 and C272. This unique intra-membrane signal-transduction pathway enables fast signaling, and triggers synchronous release by conformational-coupling of the channel with Sx1A.
Figures
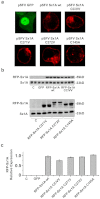


 ) or with RFP-Sx1A (
) or with RFP-Sx1A ( , left); RFP-Sx1ACC/AA (
, left); RFP-Sx1ACC/AA ( , middle-left); RFP-Sx1ACC/SS (
, middle-left); RFP-Sx1ACC/SS ( , middle-right); RFP-Sx1ACC/VV (
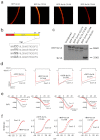
, middle-right); RFP-Sx1ACC/VV ( , right). (f) Voltage-conductance (G/Gmax) analysis of α11.2/β2/α2δ expressed either alone or with the different mutants, as indicated in B. The data points correspond to the mean ± SEM of currents (n = 12–14). Individual data points are mean ± SEM (n = 12–14). The results were fitted to the sigmoidal Boltzmann equation.
, right). (f) Voltage-conductance (G/Gmax) analysis of α11.2/β2/α2δ expressed either alone or with the different mutants, as indicated in B. The data points correspond to the mean ± SEM of currents (n = 12–14). Individual data points are mean ± SEM (n = 12–14). The results were fitted to the sigmoidal Boltzmann equation.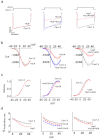
 ) or with AuF (
) or with AuF ( , left); Sx1A/Sx1A + AuF (
, left); Sx1A/Sx1A + AuF ( /
/ , middle) or Sx1A+AuF+AD4 (
, middle) or Sx1A+AuF+AD4 ( , right). Inward Ca2+ currents were evoked from a holding potential of −80 mV to various test potentials in response to 200 ms test pulse at 5 mV increments. (c) G/Gmax values as indicated in b (d) τ activation values as indicated in b. The data points correspond to the mean ± SEM of currents (n = 8–15).
, right). Inward Ca2+ currents were evoked from a holding potential of −80 mV to various test potentials in response to 200 ms test pulse at 5 mV increments. (c) G/Gmax values as indicated in b (d) τ activation values as indicated in b. The data points correspond to the mean ± SEM of currents (n = 8–15).

References
-
- Atlas D. Signaling role of the voltage-gated calcium channel as the molecular on/off-switch of secretion. Cell Signal 22, 1597–1603 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Atlas D. The Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel Functions as the Molecular Switch of Synaptic Transmission. Annu Rev Biochem 82 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Sheng Z. H., Rettig J., Takahashi M. & Catterall W. A. Identification of a syntaxin-binding site on N-type calcium channels. Neuron 13, 1303–1313 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Wiser O., Tobi D., Trus M. & Atlas D. Synaptotagmin restores kinetic properties of a syntaxin-associated N-type voltage sensitive calcium channel. FEBS Lett 404, 203–207 (1997). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

