Oxymatrine prevents NF-κB nuclear translocation and ameliorates acute intestinal inflammation
- PMID: 23568217
- PMCID: PMC3620667
- DOI: 10.1038/srep01629
Oxymatrine prevents NF-κB nuclear translocation and ameliorates acute intestinal inflammation
Abstract
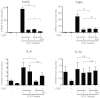
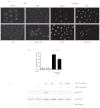
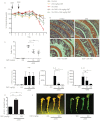
Oxymatrine is a traditional Chinese herbal product that exhibits anti-inflammatory effects in models of heart, brain and liver injury. We investigated the impact of oxymatrine in an acute model of intestinal injury and inflammation. Oxymatrine significantly decreased LPS-induced NF-κB-driven luciferase activity, correlating with diminished induction of Cxcl2, Tnfα and Il6 mRNA expression in rat IEC-6 and murine BMDC. Although oxymatrine decreased LPS-induced p65 nuclear translocation and binding to the Cxcl2 gene promoter, this effect was independent of IκBα degradation/phosphorylation. DSS-induced weight loss and histological damage were ameliorated in oxymatrine-treated C57BL/6-WT-mice. While this effect correlated with reduced colonic Il6 and Il1β mRNA accumulation, global NF-κB activity as measured in NF-κB(EGFP) mice was unaffected. Our data demonstrate that oxymatrine reduces LPS-induced NF-κB nuclear translocation and activity independently of IκBα status, prevents intestinal inflammation through blockade of inflammatory signaling and ameliorates overall intestinal inflammation in vivo.
Figures


References
-
- Kamboj V. P. Herbal medicine. Current Science 78, 35–39 (2000).
-
- Egan B., Hodgkins C., Shepherd R., Timotijevic L. & Raats M. An overview of consumer attitudes and beliefs about plant food supplements. Food Funct 2, 747–752 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Barnes P. M., Powell-Griner E., McFann K. & Nahin R. L. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults: United States, 2002. Adv Data 1–19 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Ritchie M. R. Use of herbal supplements and nutritional supplements in the UK: what do we know about their pattern of usage? Proc Nutr Soc 66, 479–482 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

