Intercellular trafficking of the nuclear oncoprotein DEK
- PMID: 23569252
- PMCID: PMC3637753
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1220751110
Intercellular trafficking of the nuclear oncoprotein DEK
Abstract
DEK is a biochemically distinct, conserved nonhistone protein that is vital to global heterochromatin integrity. In addition, DEK can be secreted and function as a chemotactic, proinflammatory factor. Here we show that exogenous DEK can penetrate cells, translocate to the nucleus, and there carry out its endogenous nuclear functions. Strikingly, adjacent cells can take up DEK secreted from synovial macrophages. DEK internalization is a heparan sulfate-dependent process, and cellular uptake of DEK into DEK knockdown cells corrects global heterochromatin depletion and DNA repair deficits, the phenotypic aberrations characteristic of these cells. These findings thus unify the extracellular and intracellular activities of DEK, and suggest that this paracrine loop involving DEK plays a role in chromatin biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
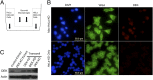
Figures
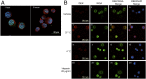
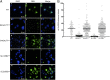
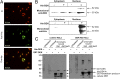
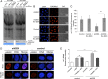
References
-
- Soares LM, Zanier K, Mackereth C, Sattler M, Valcárcel J. Intron removal requires proofreading of U2AF/3′ splice site recognition by DEK. Science. 2006;312(5782):1961–1965. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI062248/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AR056748/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AR-056748-01/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI087128/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5-P30-AR-048310-07/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32-CA-88784-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR055620/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR-055620/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR048310/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA088784/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

