Effect of verapamil on systemic exposure and safety of umeclidinium and vilanterol: a randomized and open-label study
- PMID: 23569370
- PMCID: PMC3615930
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S40859
Effect of verapamil on systemic exposure and safety of umeclidinium and vilanterol: a randomized and open-label study
Abstract
Background: The combination of umeclidinium (UMEC), a long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonist, and vilanterol (VI), a selective long-acting β₂ agonist, is in development for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This study evaluated the pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability, and pharmacodynamics of once-daily, inhaled UMEC and UMEC/VI when co-administered with oral verapamil, a moderate P-glycoprotein transporter and moderate cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitor frequently used by patients with COPD and cardiovascular comorbidities.
Methods: Subjects were randomized to one of two 13-day treatment regimens: UMEC 500 μg or UMEC 500 μg/VI 25 μg. All subjects received a single tablet containing 240 mg verapamil on each of days 9-13.
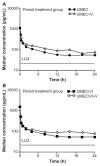
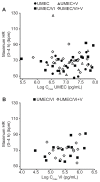
Results: Repeat doses of UMEC and UMEC/VI in combination with and without verapamil were safe and well tolerated. There was no increase in systemic exposure of UMEC when administered in combination with VI compared to UMEC alone. UMEC maximum concentration was similar with or without verapamil; a moderate increase in UMEC area under the curve (approximately 1.4-fold) was observed with verapamil. Verapamil did not increase systemic exposure to VI following administration of the UMEC/VI combination.
Conclusion: Administration of UMEC and UMEC/VI combination was well tolerated and did not show clinically relevant increases in systemic exposure for either drug. The UMEC/VI combination is unlikely to have a clinically meaningful drug-drug interaction with moderate P-glycoprotein transporter and CYP3A4 inhibitor drugs.
Keywords: long-acting muscarinic antagonist; long-acting β2 agonist; umeclidinium; verapamil; vilanterol.
Figures
References
-
- Mannino DM, Braman S. The epidemiology and economics of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2007;4(7):502–506. - PubMed
-
- Halbert RJ, Natoli JL, Gano A, Badamgarav E, Buist AS, Mannino DM. Global burden of COPD: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. 2006;28(3):523–532. - PubMed
-
- Ng TP, Niti M, Fones C, Yap KB, Tan WC. Co-morbid association of depression and COPD: a population-based study. Respir Med. 2009;103(6):895–901. - PubMed
-
- Foster TS, Miller JD, Marton JP, Caloyeras JP, Russell MW, Menzin J. Assessment of the economic burden of COPD in the US: a review and synthesis of the literature. COPD. 2006;3(4):211–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

