Pedalium murex Linn (Pedaliaceae) fruits: a comparative antioxidant activity of its different fractions
- PMID: 23569800
- PMCID: PMC3614206
- DOI: 10.1016/S2221-1691(11)60087-7
Pedalium murex Linn (Pedaliaceae) fruits: a comparative antioxidant activity of its different fractions
Abstract
Objective: To examine the antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of different solvent fractions of Pedalium murex (P. murex) Linn fruits (Family: Pedaliaceae) as well as the correlation between the total antioxidant capacity and total phenolic content.
Methods: In the present study, the antioxidant activities of P. murex were evaluated using six in-vitro assays, namely total antioxidant assay, DPPH assay, reducing power, nitric oxide scavenging, hydrogen peroxide scavenging and deoxyribose scavenging assays, and total phenol contents were also investigated.
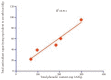
Results: The ethyl acetate (EA) fraction was found to have high levels of phenolic content (298.72±2.09 mg GAE/g). The EA fraction exhibit higher total antioxidant capacity, higher percentage of DPPH radical scavenging activity (135.11±2.95µg/mL), nitric oxide (200.57±4.51µg/mL), hydrogen peroxide (217.91±6.12 µg/mL), deoxyribose (250.01±4.68µg/mL) and higher reducing power. Correlation coefficient (r(2) =0.914) was found to be significant between total phenolic content and total antioxidant activity.
Conclusions: In general, the results indicate that the EA fractions are rich in phenolic antioxidants with potent free radical scavenging activity implying their importance to human health.
Keywords: Antioxidant activity; Different solvent fraction; In vitro assay; Pedalium murex; Scavenging activity; Total phenolics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Matkowski A, Zielinska S, Oszmianski J, Lamer-Zarawska E. Antioxidant activity of extracts from leaves and roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, S. przewalskii Maxim, and S. verticillata L. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99(16):7892–7896. - PubMed
-
- Tepe B. Antioxidant potentials and rosmarinic acid levels of the methanolic extracts of Salvia virgata (Jacq), Salvia staminea (Montbret and Aucher ex Bentham) and Salvia verbenaca (L.) from Turkey. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99(6):1584–1588. - PubMed
-
- Zhao GR, Xiang ZJ, Ye TY, Yuan YJ, Guo ZX. Antioxidant activities of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Panax notoginseng. Food Chem. 2006;99(4):767–774.
-
- Wannes WA, Mhamdi B, Sriti J, Jemia MB, Ouchikh O, Hamdaoui G, et al. et al. Antioxidant activities of the essential oils and methanol extracts from myrtle (Myrtus communis var. italica L.) leaf, stem and flower. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48(5):1362–1370. - PubMed
-
- Grzegorczyk I, Matkowski A, Wysokińska H. Antioxidant activity of extracts from in vitro cultures of Salvia officinalis L. Food Chem. 2007;104(2):536–541.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

