Diabetes abrogates sex differences and aggravates cardiometabolic risk in postmenopausal women
- PMID: 23570342
- PMCID: PMC3626922
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-61
Diabetes abrogates sex differences and aggravates cardiometabolic risk in postmenopausal women
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of gender and menopause in cardiometabolic risk in a type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) population, based on classical and non-traditional markers.
Methods: Seventy four volunteers and 110 T2DM patients were enrolled in the study. Anthropometric data, blood pressure, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC) and the following serum markers were analyzed: glucose, Total-c, TGs, LDL-c, Oxidized-LDL, total HDL-c and large and small HDL-c subpopulations, paraoxonase 1 activity, hsCRP, uric acid, TNF-α, adiponectin and VEGF.
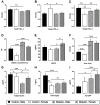
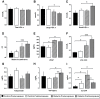
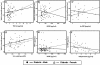
Results: Non-diabetic women, compared to men, presented lower glycemia, WC, small HDL-c, uric acid, TNF-α and increased large HDL-c. Diabetes abrogates the protective effect of female gender, since diabetic women showed increased BMI, WC, small HDL-c, VEGF, uric acid, TNF-α and hsCRP, as well as reduced adiponectin, when compared with non-diabetic. In diabetic females, but not in males, WC is directly and significantly associated with TNF-α, VEGF, hsCRP and uric acid; TNF-α is directly associated with VEGF and hsCRP, and inversely with adiponectin. Postmenopausal females presented a worsen cardiometabolic profile, viewed by the increased WC, small HDL-c, VEGF, uric acid, TNF-α and hsCRP. In this population, WC is directly and significantly associated with TNF-α, VEGF, hsCRP; TNF-α is directly associated with VEGF; and uric acid is inversely associated with large HDL-c and hsCRP with adiponectin, also inversely.
Conclusions: Diabetes abrogates the protective effect of gender on non-diabetic women, and postmenopausal diabetic females presented worsen cardiometabolic risk, including a more atherogenic lipid sketch and a pro-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic profile. The classical cardiovascular risk factors (CVRFs) fail to completely explain these differences, which are better clarified using "non-traditional" factors, such as HDL-c subpopulations, rather than total HDL-c content, and markers of inflammation and angiogenesis, namely TNF-α, hsCRP, uric acid and VEGF. Multi-therapeutic intervention, directed to obesity, atherogenic lipid particles and inflammatory mediators is advisory in order to efficiently prevent the serious diabetic cardiovascular complications.
Figures

References
-
- Barr EL, Zimmet PZ, Welborn TA, Jolley D, Magliano DJ, Dunstan DW, Cameron AJ, Dwyer T, Taylor HR, Tonkin AM, Wong TY, McNeil J, Shaw JE. Risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in individuals with diabetes mellitus, impaired fasting glucose, and impaired glucose tolerance: the Australian Diabetes, Obesity, and Lifestyle Study (AusDiab) Circulation. 2007;116(2):151–157. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.685628. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cortez-Dias N, Martins S, Belo A, Fiuza M. VALSIM. Prevalence, management and control of diabetes mellitus and associated risk factors in primary health care in Portugal. Rev Port Cardiol. 2010;29(4):509–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

