NF-kB overexpression and decreased immunoexpression of AR in the muscular layer is related to structural damages and apoptosis in cimetidine-treated rat vas deferens
- PMID: 23570504
- PMCID: PMC3727959
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-11-29
NF-kB overexpression and decreased immunoexpression of AR in the muscular layer is related to structural damages and apoptosis in cimetidine-treated rat vas deferens
Abstract
Background: Cimetidine, histamine H2 receptors antagonist, has caused adverse effects on the male hormones and reproductive tract due to its antiandrogenic effect. In the testes, peritubular myoid cells and muscle vascular cells death has been associated to seminiferous tubules and testicular microvascularization damages, respectively. Either androgen or histamine H2 receptors have been detected in the mucosa and smooth muscular layer of vas deferens. Thus, the effect of cimetidine on this androgen and histamine-dependent muscular duct was morphologically evaluated.
Methods: The animals from cimetidine group (CMTG; n=5) received intraperitoneal injections of 100 mg/kg b.w. of cimetidine for 50 days; the control group (CG) received saline solution. The distal portions of vas deferens were fixed in formaldehyde and embedded in paraffin. Masson´s trichrome-stained sections were subjected to morphological and the following morphometrical analyzes: epithelial perimeter and area of the smooth muscular layer. TUNEL (Terminal deoxynucleotidyl-transferase mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling) method, NF-kB (nuclear factor kappa B) and AR (androgen receptors) immunohistochemical detection were also carried out. The birefringent collagen of the muscular layer was quantified in picrosirius red-stained sections under polarized light. The muscular layer was also evaluated under Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM).
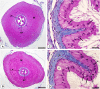
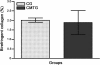
Results: In CMTG, the mucosa of vas deferens was intensely folded; the epithelial cells showed numerous pyknotic nuclei and the epithelial perimeter and the area of the muscular layer decreased significantly. Numerous TUNEL-labeled nuclei were found either in the epithelial cells, mainly basal cells, or in the smooth muscle cells which also showed typical features of apoptosis under TEM. While an enhanced NF-kB immunoexpression was found in the cytoplasm of muscle cells, a weak AR immunolabeling was detected in these cells. In CMTG, no significant difference was observed in the birefringent collagen content of the muscular layer in comparison to CG.
Conclusions: Cimetidine induces significant damages in the epithelium; a possible antiandrogenic effect on the basal cells turnover should be considered. The cimetidine-induced muscle cells apoptosis confirms the susceptibility of these cells to this drug. The parallelism between enhanced cytoplasmic NF-kB immunolabeling in the damaged muscular tissue and muscle cell apoptosis suggests that this drug may avoid the translocation of NF-kB to the nucleus and interfere in the control of NF-kB-mediated smooth muscle cell apoptosis. The decreased immunoexpression of ARs verified in the damaged muscular tissue reinforces this possibility.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Increased apoptosis in osteoclasts and decreased RANKL immunoexpression in periodontium of cimetidine-treated rats.J Anat. 2013 Feb;222(2):239-47. doi: 10.1111/joa.12011. Epub 2012 Dec 2. J Anat. 2013. PMID: 23198931 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced ERbeta immunoexpression and apoptosis in the germ cells of cimetidine-treated rats.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009 Nov 18;7:127. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-7-127. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19922658 Free PMC article.
-
Cimetidine-induced vascular cell apoptosis impairs testicular microvasculature in adult rats.Histol Histopathol. 2012 Oct;27(10):1343-51. doi: 10.14670/HH-27.1343. Histol Histopathol. 2012. PMID: 22936453
-
Vitamin B12 supplement exerts a beneficial effect on the seminiferous epithelium of cimetidine-treated rats.Cells Tissues Organs. 2011;193(3):184-94. doi: 10.1159/000319371. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Cells Tissues Organs. 2011. PMID: 20962501
-
Morphological evidences indicate that the interference of cimetidine on the peritubular components is responsible for detachment and apoptosis of Sertoli cells.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2008 May 9;6:18. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-6-18. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18471284 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Isoflavone Protects the Renal Tissue of Diabetic Ovariectomized Rats via PPARγ.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 21;14(13):2567. doi: 10.3390/nu14132567. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35807748 Free PMC article.
-
Chondroitin Sulfate Protects the Liver in an Experimental Model of Extra-Hepatic Cholestasis Induced by Common Bile Duct Ligation.Molecules. 2022 Jan 20;27(3):654. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030654. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35163920 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced In Vivo Wound Healing Efficacy of a Novel Piperine-Containing Bioactive Hydrogel in Excision Wound Rat Model.Molecules. 2023 Jan 5;28(2):545. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020545. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677613 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic administration of curcumin or piperine enhances the periodontal repair: a preliminary study in rats.Clin Oral Investig. 2019 Aug;23(8):3297-3306. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2755-9. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Clin Oral Investig. 2019. PMID: 30498979
-
Effects of estrogen deficiency followed by streptozotocin-induced diabetes on periodontal tissues of female rats.J Mol Histol. 2020 Aug;51(4):353-365. doi: 10.1007/s10735-020-09885-6. Epub 2020 Jun 3. J Mol Histol. 2020. PMID: 32488735
References
-
- Zhou Q, Nie R, Prins SG, Saunders PTK, Katzenellenbogen BS, Hess RA. Localization of androgen and estrogen receptors in adult male mouse reproductive tract. JAndrol. 2002;23:870–881. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

