Neurobiological underpinnings of math and reading learning disabilities
- PMID: 23572008
- PMCID: PMC3795983
- DOI: 10.1177/0022219413483174
Neurobiological underpinnings of math and reading learning disabilities
Abstract
The primary goal of this review is to highlight current research and theories describing the neurobiological basis of math (MD), reading (RD), and comorbid math and reading disability (MD+RD). We first describe the unique brain and cognitive processes involved in acquisition of math and reading skills, emphasizing similarities and differences in each domain. Next we review functional imaging studies of MD and RD in children, integrating relevant theories from experimental psychology and cognitive neuroscience to characterize the functional neuroanatomy of cognitive dysfunction in MD and RD. We then review recent research on the anatomical correlates of MD and RD. Converging evidence from morphometry and tractography studies are presented to highlight distinct patterns of white matter pathways which are disrupted in MD and RD. Finally, we examine how the intersection of MD and RD provides a unique opportunity to clarify the unique and shared brain systems which adversely impact learning and skill acquisition in MD and RD, and point out important areas for future work on comorbid learning disabilities.
Keywords: comorbidity; learning disabilities; neurobiological.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures




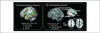
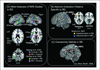
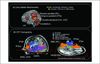
References
-
- Ahissar M. Dyslexia and the anchoring-deficit hypothesis. Trend in Cognitive Science. 2007;11(11):458–465. - PubMed
-
- Ansari D. Effects of development and enculturation on number representation in the brain. Nature Review Neuroscience. 2008;9(4):278–291. - PubMed
-
- Ansari D, Dhital B. Age-related changes in the activation of the intraparietal sulcus during nonsymbolic magnitude processing: An event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2006;18(11):1820–1828. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

