Assessment of carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with microalbuminuria by high-frequency ultrasonography
- PMID: 23573090
- PMCID: PMC3612477
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/819584
Assessment of carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with microalbuminuria by high-frequency ultrasonography
Abstract
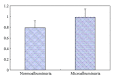
The aim of this study is to evaluate carotid atherosclerosis in patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus with microalbuminuria (MA) by high-frequency ultrasonography. Two hundred and fifty patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus were divided into two groups according to urinary albumin excretion rate (UAER): normoalbuminuria group (130 cases) and microalbuminuria group (120 cases). The intimal-medial thickness (IMT) and the atherosclerotic plaques of carotid artery were observed in both groups by high-frequency ultrasound. Fasting blood glucose (FBG), hemoglobin A1c, and lipid profiles were measured. The values of IMT of microalbuminuria group were significantly higher than those of normoalbuminuria group (P < 0.05). In univariate analysis, IMT was positively and significantly associated with age (r = 0.265, P < 0.05), waist circumference (r = 0.263, P < 0.05), body mass index (r = 0.285, P < 0.05), systolic blood pressure (r = 0.276, P < 0.05), UAER (r = 0.359, P < 0.05), HbA1c (r = 0.462, P < 0.05) and, duration of diabetes (r = 0.370, P < 0.05). In multivariate linear regression analysis, UAER and HbA1c were independent predictors of IMT (P < 0.05 for all). In the two groups, the rate of soft plaques was higher than that of dense plaques and calcified plaques. In conclusion, there is a significant association between microalbuminuria and IMT which is regarded as the early sign of carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetic patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Subclinical atherosclerosis is increased in type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria evaluated by intima-media thickness and pulse wave velocity.Kidney Int. 2004 Jul;66(1):448-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00752.x. Kidney Int. 2004. PMID: 15200455
-
Association of microalbuminuria with carotid intima-media thickness and coronary artery disease--a cross-sectional study in Western India.J Assoc Physicians India. 2002 Sep;50:1124-9. J Assoc Physicians India. 2002. PMID: 12516693
-
Association between microalbuminuria and subclinical atherosclerosis evaluated by carotid artery intima-media in elderly patients with normal renal function.BMC Nephrol. 2012 Jun 11;13:37. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-13-37. BMC Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22686733 Free PMC article.
-
A new marker of carotid atherosclerosis in middle aged adults: cystatin C or microalbuminuria.Indian Heart J. 2010 Jul-Aug;62(4):320-3. Indian Heart J. 2010. PMID: 21280472
-
Decrease in glomerular filtration rate in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes is linked to atherosclerosis.Diabetes Care. 1998 Nov;21(11):1848-55. doi: 10.2337/diacare.21.11.1848. Diabetes Care. 1998. PMID: 9802732
Cited by
-
Poor lung function has inverse relationship with microalbuminuria, an early surrogate marker of kidney damage and atherosclerosis: the 5th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 9;9(4):e94125. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094125. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24718679 Free PMC article.
-
Aortic Stiffness Index And Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Are Independently Associated With The Presence Of Microalbuminuria In Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019 Sep 19;12:1889-1896. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S223880. eCollection 2019. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019. PMID: 31571963 Free PMC article.
-
Indoor air pollution and its association with poor lung function, microalbuminuria and variations in blood pressure among kitchen workers in India: a cross-sectional study.Environ Health. 2017 Apr 4;16(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12940-017-0243-3. Environ Health. 2017. PMID: 28376835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995–2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(9):1414–1431. - PubMed
-
- Mogensen CE, Damsgaard EM, Froland A, Nielsen S, Olivarius NDF, Schmitz A. Microalbuminuria in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Clinical Nephrology. 1992;38(supplement 1):S28–S39. - PubMed
-
- Dinneen SF, Gerstein HC. The association of microalbuminuria and mortality in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a systematic overview of the literature. Archives of Internal Medicine. 1997;157(13):1413–1418. - PubMed
-
- Stehouwer CDA, Gall MA, Twisk JWR, Knudsen E, Emeis JJ, Parving HH. Increased urinary albumin excretion, endothelial dysfunction, and chronic low-grade inflammation in type 2 diabetes: progressive, interrelated, and independently associated with risk of death. Diabetes. 2002;51(4):1157–1165. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources