Qushi Huayu Decoction Inhibits Hepatic Lipid Accumulation by Activating AMP-Activated Protein Kinase In Vivo and In Vitro
- PMID: 23573117
- PMCID: PMC3614185
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/184358
Qushi Huayu Decoction Inhibits Hepatic Lipid Accumulation by Activating AMP-Activated Protein Kinase In Vivo and In Vitro
Abstract
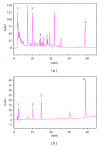
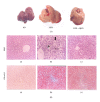
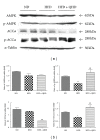
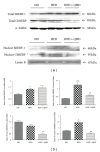
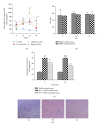
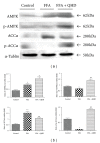
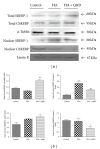
Qushi Huayu Decoction (QHD), a Chinese herbal formula, has been proven effective on alleviating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in human and rats. The present study was conducted to investigate whether QHD could inhibit hepatic lipid accumulation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in vivo and in vitro. Nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) model was duplicated with high-fat diet in rats and with free fatty acid (FFA) in L02 cells. In in vivo experimental condition, QHD significantly decreased the accumulation of fatty droplets in livers, lowered low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels in serum. Moreover, QHD supplementation reversed the HFD-induced decrease in the phosphorylation levels of AMPK and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and decreased hepatic nuclear protein expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP-1) and carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP) in the liver. In in vitro, QHD-containing serum decreased the cellular TG content and alleviated the accumulation of fatty droplets in L02 cells. QHD supplementation reversed the FFA-induced decrease in the phosphorylation levels of AMPK and ACC and decreased the hepatic nuclear protein expression of SREBP-1 and ChREBP. Overall results suggest that QHD has significant effect on inhibiting hepatic lipid accumulation via AMPK pathway in vivo and in vitro.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition on XBP1s-driven lipogenesis by Qushi Huayu Decoction contributes to amelioration of hepatic steatosis induced by fructose.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jan 30;301:115806. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115806. Epub 2022 Oct 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36216198
-
[Effect of qushl huayu decoction on high-fat diet induced hepatic lipid deposition in rate].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2009 Dec;29(12):1092-5. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 20214330 Chinese.
-
[The role of adiponectin and adiponectin receptor 2 in the pathology of fatty liver].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2009 Nov;17(11):826-30. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19958641 Chinese.
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544542. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30580553 Review.
-
Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on metabolic syndrome.J Ginseng Res. 2021 May;45(3):380-389. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.11.002. Epub 2020 Nov 12. J Ginseng Res. 2021. PMID: 34025131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Triglyceride: A mediator of the association between waist-to-height ratio and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A second analysis of a population-based study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 31;13:973823. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.973823. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36387881 Free PMC article.
-
Qushi Huayu decoction attenuated hepatic lipid accumulation via JAK2/STAT3/CPT-1A-related fatty acid β-oxidation in mice with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):2124-2133. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2134898. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 36308318 Free PMC article.
-
QSHY Granules Promote White Adipose Tissue Browning and Correct BCAAs Metabolic Disorder in NAFLD Mice.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 Oct 14;14:4241-4251. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S332659. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 34703257 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota modulation by Traditional Chinese Medicine: a translational strategy for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 10;16:1600439. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1600439. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40556760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geniposide and Chlorogenic Acid Combination Improves Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Involving the Potent Suppression of Elevated Hepatic SCD-1.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 4;12:653641. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.653641. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34017254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Targher G, Chonchol M, Pichiri I, Zoppini G. Risk of cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease in diabetic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: just a coincidence? Journal of Endocrinological Investigation. 2011;34:544–551. - PubMed
-
- Lewis JR, Mohanty SR. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a review and update. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 2010;55(3):560–578. - PubMed
-
- Torres DM, Williams CD, Harrison SA. Features, diagnosis, and treatment of nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2012;10:837–858. - PubMed
-
- Postic C, Girard J. The role of the lipogenic pathway in the development of hepatic steatosis. Diabetes & Metabolism. 2008;34(6):643–648. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

