Electroacupuncture Reduces Carrageenan- and CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain Accompanied by Changing the Expression of Nav1.7 and Nav1.8, rather than Nav1.9, in Mice Dorsal Root Ganglia
- PMID: 23573123
- PMCID: PMC3615619
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/312184
Electroacupuncture Reduces Carrageenan- and CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain Accompanied by Changing the Expression of Nav1.7 and Nav1.8, rather than Nav1.9, in Mice Dorsal Root Ganglia
Abstract
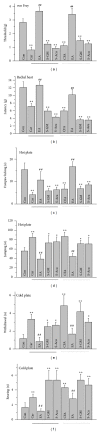
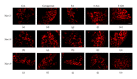
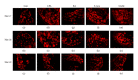
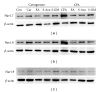
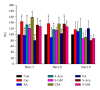
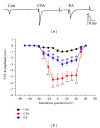
Several voltage-gated sodium channels (Navs) from nociceptive nerve fibers have been identified as important effectors in pain signaling. The objective of this study is to investigate the electroacupuncture (EA) analgesia mechanism by changing the expression of Navs in mice dorsal root ganglia (DRG). We injected carrageenan and complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) into the mice plantar surface of the hind paw to induce inflammation and examined the antinociception effect of EA at the Zusanli (ST36) acupoint at 2 Hz low frequency. Mechanical hyperalgesia was evaluated by using electronic von Frey filaments, and thermal hyperalgesia was assessed using Hargreaves' test. Furthermore, we observed the expression and quality of Navs in DRG neurons. Our results showed that EA reduced mechanical and thermal pain in inflammatory animal model. The expression of Nav1.7 and Nav1.8 was increased after 4 days of carrageenan- and CFA-elicited inflammatory pain and further attenuated by 2 Hz EA stimulation. The attenuation cannot be observed in Nav1.9 sodium channels. We demonstrated that EA at Zusanli (ST36) acupoint at 2 Hz low-frequency stimulation attenuated inflammatory pain accompanied by decreasing the expression of Nav1.7 and 1.8, rather than Nav1.9, sodium channels in peripheral DRG neurons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucocorticoid Receptor Contributes to Electroacupuncture-Induced Analgesia by Inhibiting Nav1.7 Expression in Rats With Inflammatory Pain Induced by Complete Freund's Adjuvant.Neuromodulation. 2022 Dec;25(8):1393-1402. doi: 10.1111/ner.13499. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Neuromodulation. 2022. PMID: 34337820
-
Acid-sensing ion channel 3 mediates peripheral anti-hyperalgesia effects of acupuncture in mice inflammatory pain.J Biomed Sci. 2011 Nov 9;18(1):82. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-18-82. J Biomed Sci. 2011. PMID: 22070775 Free PMC article.
-
The specialised pro-resolving lipid mediator maresin 1 reduces inflammatory pain with a long-lasting analgesic effect.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Jun;176(11):1728-1744. doi: 10.1111/bph.14647. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30830967 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the Effects and Mechanisms of Electroacupuncture at Ipsilateral or Contralateral ST36-ST37 Acupoints on CFA-induced Inflammatory Pain.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 24;6:22123. doi: 10.1038/srep22123. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26906464 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications of voltage-gated sodium channels in chronic pain syndromes.Front Pharmacol. 2015 Nov 5;6:263. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00263. eCollection 2015. Front Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26594175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture induces antihyperalgesic effect through endothelin-B receptor in the chronic phase of a mouse model of complex regional pain syndrome type I.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Dec;470(12):1815-1827. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2192-2. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 30094478
-
Electroacupuncture Inhibits the Activation of p38MAPK in the Central Descending Facilitatory Pathway in Rats with Inflammatory Pain.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:7531060. doi: 10.1155/2017/7531060. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 29358970 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan Oligosaccharide Reduces Propofol Requirements and Propofol-Related Side Effects.Mar Drugs. 2016 Dec 21;14(12):234. doi: 10.3390/md14120234. Mar Drugs. 2016. PMID: 28009824 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Acupuncture on the p38 Signaling Pathway in Several Nervous System Diseases: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 30;21(13):4693. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134693. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32630156 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture alleviates retrieval of pain memory and its effect on phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein in anterior cingulate cortex in rats.Behav Brain Funct. 2015 Mar 4;11:9. doi: 10.1186/s12993-015-0055-y. Behav Brain Funct. 2015. PMID: 25886521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker MD, Bostock H. Low-threshold, persistent sodium current in rat large dorsal root ganglion neurons in culture. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1997;77(3):1503–1513. - PubMed
-
- Black JA, Liu S, Tanaka M, Cummins TR, Waxman SG. Changes in the expression of tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels within dorsal root ganglia neurons in inflammatory pain. Pain. 2004;108(3):237–247. - PubMed
-
- Crill WE. Persistent sodium current in mammalian central neurons. Annual Review of Physiology. 1996;58:349–362. - PubMed
-
- Baker MD, Wood JN. Involvement of Na+ channels in pain pathways. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 2001;22(1):27–31. - PubMed
-
- Black JA, Dib-Hajj S, McNabola K, et al. Spinal sensory neurons express multiple sodium channel α-subunit mRNAs. Molecular Brain Research. 1996;43(1-2):117–131. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

