Evaluation of In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activities and Protective Effect of Fermented Preparations of Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae on Intestinal Barrier Function against Lipopolysaccharide Insult
- PMID: 23573125
- PMCID: PMC3612467
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/363076
Evaluation of In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activities and Protective Effect of Fermented Preparations of Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae on Intestinal Barrier Function against Lipopolysaccharide Insult
Abstract
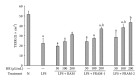
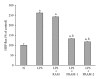
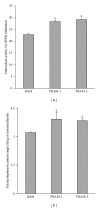
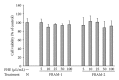
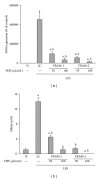
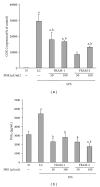
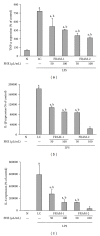
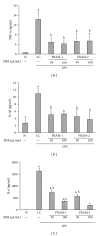
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a potent inducer of systemic inflammatory responses, is known to cause impairment of intestinal barrier function. Here, we evaluated the in vitro protective effect of an unfermented formulation of Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae (RAM), a traditional Chinese herbal medicine widely used in the treatment of many digestive and gastrointestinal disorders, and two fermented preparations of RAM, designated as FRAM-1 (prepared in Luria-Bertani broth) and FRAM-2 (prepared in glucose), on intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) against LPS insult. In general, fermented formulations, especially FRAM-2, but not unfermented RAM, exerted an appreciable protective effect on IECs against LPS-induced perturbation of membrane resistance and permeability. Both fermented formulations exhibited appreciable anti-inflammatory activities in terms of their ability to inhibit LPS-induced gene expression and induced production of a number of key inflammatory mediators and cytokines in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. However, in most cases, FRAM-2 exhibited stronger anti-inflammatory effects than FRAM-1. Our findings also suggest that suppression of nuclear factor- κ β (NF- κ β ) activity might be one of the possible mechanisms by which the fermented RAM exerts its anti-inflammatory effects. Collectively, our results highlight the benefits of using fermented products of RAM to protect against LPS-induced inflammatory insult and impairment in intestinal barrier function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fermented Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae alleviates high fat diet-induced obesity in association with regulation of intestinal permeability and microbiota in rats.Sci Rep. 2015 Feb 16;5:8391. doi: 10.1038/srep08391. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25684573 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo protective effects of fermented preparations of dietary herbs against lipopolysaccharide insult.Food Chem. 2012 Sep 15;134(2):758-65. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.02.175. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 23107688
-
Evaluation of the in vitro and in vivo protective effects of unfermented and fermented Rhizoma coptidis formulations against lipopolysaccharide insult.Food Chem. 2012 Nov 15;135(2):452-9. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.05.007. Epub 2012 May 11. Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22868113
-
Rhizoma Atractylodis macrocephalae: a review of photochemistry, pharmacokinetics and pharmacology.Pharmazie. 2020 Mar 20;75(2):42-55. doi: 10.1691/ph.2020.9738. Pharmazie. 2020. PMID: 32213234 Review.
-
Polysaccharides from Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae: A Review on Their Extraction, Purification, Structure, and Bioactivities.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Aug 17;2022:2338533. doi: 10.1155/2022/2338533. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36034948 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The beneficial effect of peppermint (Mentha X Piperita L.) and lemongrass (Melissa officinalis L.) dosage on total antioxidant and polyphenol content during alcoholic fermentation.Food Chem X. 2022 Jan 23;13:100226. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100226. eCollection 2022 Mar 30. Food Chem X. 2022. PMID: 35499003 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro antiproliferative studies of extracts of the marine molluscs: Tympanatonus fuscatus Var radula (linnaeus) and Pachymelania aurita (muller).Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Apr 15;10(1):1-8. eCollection 2019. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31149366 Free PMC article.
-
Erchen Decoction and Linguizhugan Decoction Ameliorate Hepatic Insulin Resistance by Inhibiting IRS-1Ser307 Phosphorylation In Vivo and In Vitro.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:1589871. doi: 10.1155/2017/1589871. Epub 2017 May 29. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28630632 Free PMC article.
-
Rotula aquatica Lour attenuates secretion of proinflammatory mediators and cytokines in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in murine RAW 264.7 macrophages.Inflammopharmacology. 2018 Feb;26(1):29-38. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0420-6. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Inflammopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29159716
-
Intervening TNF-α via PPARγ with Gegenqinlian Decoction in Experimental Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:715638. doi: 10.1155/2015/715638. Epub 2015 Jun 28. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26221176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anand RJ, Leaphart CL, Mollen KP, Hackam DJ. The role of the intestinal barrier in the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis. Shock. 2007;27(2):124–133. - PubMed
-
- Deitch EA, Berg R, Specian R. Endotoxin promotes the translocation of bacteria from the gut. Archives of Surgery. 1987;122(2):185–190. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

