Cardioprotective Effects of Quercetin in Cardiomyocyte under Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 23573126
- PMCID: PMC3612448
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/364519
Cardioprotective Effects of Quercetin in Cardiomyocyte under Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
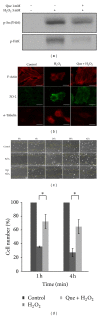
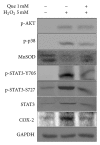
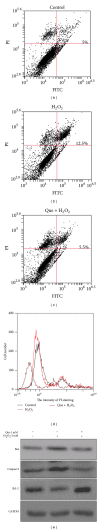
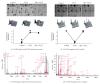
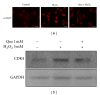
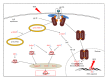
Quercetin, a polyphenolic compound existing in many vegetables, fruits, has antiinflammatory, antiproliferation, and antioxidant effect on mammalian cells. Quercetin was evaluated for protecting cardiomyocytes from ischemia/reperfusion injury, but its protective mechanism remains unclear in the current study. The cardioprotective effects of quercetin are achieved by reducing the activity of Src kinase, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), caspase 9, Bax, intracellular reactive oxygen species production, and inflammatory factor and inducible MnSOD expression. Fluorescence two-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis (2D-DIGE) and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) can reveal the differentially expressed proteins of H9C2 cells treated with H2O2 or quercetin. Although 17 identified proteins were altered in H2O2-induced cells, these proteins such as alpha-soluble NSF attachment protein ( α -SNAP), Ena/VASP-like protein (Evl), and isopentenyl-diphosphate delta-isomerase 1 (Idi-1) were reverted by pretreatment with quercetin, which correlates with kinase activation, DNA repair, lipid, and protein metabolism. Quercetin dephosphorylates Src kinase in H2O2-induced H9C2 cells and likely blocks the H2O2-induced inflammatory response through STAT3 kinase modulation. This probably contributes to prevent ischemia/reperfusion injury in cardiomyocytes.
Figures




References
-
- Takano H, Zou Y, Hasegawa H, Akazawa H, Nagai T, Komuro I. Oxidative stress-induced signal transduction pathways in cardiac myocytes: involvement of ROS in heart diseases. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling. 2003;5(6):789–794. - PubMed
-
- Chou HC, Chen YW, Lee TR, et al. Proteomics study of oxidative stress and Src kinase inhibition in H9C2 cardiomyocytes: a cell model of heart ischemia-reperfusion injury and treatment. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2010;49(1):96–108. - PubMed
-
- Rusnak F, Reiter T. Sensing electrons: protein phosphatase redox regulation. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 2000;25(11):527–529. - PubMed
-
- Boots AW, Haenen GRMM, Bast A. Health effects of quercetin: from antioxidant to nutraceutical. European Journal of Pharmacology. 2008;585(2-3):325–337. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

