The protective effect of alpha-lipoic Acid in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury is mediated by heme oxygenase-1
- PMID: 23573137
- PMCID: PMC3614055
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/590363
The protective effect of alpha-lipoic Acid in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury is mediated by heme oxygenase-1
Abstract
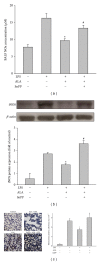
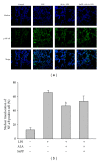
Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), occurring naturally in human food, is known to possess antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) has been reported to exhibit a therapeutic effect in several inflammatory diseases. The aim of study was to test the hypothesis that the protection of ALA against lipopolysaccharide-(LPS-) induced acute lung injury (ALI) is mediated by HO-1. Pre- or posttreatment with ALA significantly inhibited LPS-induced histological alterations of ALI, lung tissue edema, and production of proinflammatory cytokine, cytokine inducible neutrophil chemoattractant-3, and nitrite/nitrate in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. In addition, the inflammatory responses including elevation of superoxide formation, myeloperoxidase activity, polymorphonuclear neutrophils infiltration, nitrotyrosine, inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF- κ B) activation in lung tissues of LPS-instilled rats were also markedly reduced by ALA. Interestingly, treatment with ALA significantly increased nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) activation and HO-1 expression in lungs of ALI. However, blocking HO-1 activity by tin protoporphyrin IX (SnPP), an HO-1 inhibitor, markedly abolished these beneficial effects of ALA in LPS-induced ALI. These results suggest that the protection mechanism of ALA may be through HO-1 induction and in turn suppressing NF- κ B-mediated inflammatory responses.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Baicalein, an active component of Scutellaria baicalensis, protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Apr 11;153(1):197-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.02.010. Epub 2014 Feb 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24534526
-
Inhibition of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Role of Nrf2/HO-1 signal axis in inhibition of NLRP3 activation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Apr 30;551:7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.03.009. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33713981
-
Picrasma quassiodes (D. Don) Benn. attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Sep;38(3):834-44. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2669. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27431288
-
Cordycepin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2018 Jul;60:18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.04.032. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29702279
-
Acacetin attenuates mice endotoxin-induced acute lung injury via augmentation of heme oxygenase-1 activity.Inflammopharmacology. 2018 Apr;26(2):635-643. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0398-0. Epub 2017 Oct 7. Inflammopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28988328
Cited by
-
Ginsenoside Rh2 Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Raf-1/MEK/ERK, and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Mice.Nutrients. 2018 Sep 1;10(9):1208. doi: 10.3390/nu10091208. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30200495 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of lipoic acid on immune function, the antioxidant defense system, and inflammation-related genes expression of broiler chickens fed aflatoxin contaminated diets.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Apr 2;15(4):5649-62. doi: 10.3390/ijms15045649. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24699046 Free PMC article.
-
Thymus vulgaris alleviates UVB irradiation induced skin damage via inhibition of MAPK/AP-1 and activation of Nrf2-ARE antioxidant system.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Feb;21(2):336-348. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12968. Epub 2016 Sep 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 27641753 Free PMC article.
-
The Alpha-Lipoic Acid Improves Survival and Prevents Irinotecan-Induced Inflammation and Intestinal Dysmotility in Mice.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Nov 3;13(11):361. doi: 10.3390/ph13110361. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33152996 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of alpha lipoic acid co-administration on structural and immunohistochemical changes in subcutaneous tissue of anterior abdominal wall of adult male albino rat in response to polypropylene mesh implantation.Int J Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun;96(3):172-82. doi: 10.1111/iep.12127. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Int J Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25891652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E, et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. New England Journal of Medicine. 2005;353(16):1685–1693. - PubMed
-
- Tsushima K, King LS, Aggarwal NR, De Gorordo A, D’Alessio FR, Kubo K. Acute lung injury review. Internal Medicine. 2009;48(9):621–630. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Bai C, Wang X. The value of the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury model in respiratory medicine. Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine. 2010;4(6):773–783. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

