Triptolide Prevents Bone Destruction in the Collagen-Induced Arthritis Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Targeting RANKL/RANK/OPG Signal Pathway
- PMID: 23573139
- PMCID: PMC3610373
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/626038
Triptolide Prevents Bone Destruction in the Collagen-Induced Arthritis Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Targeting RANKL/RANK/OPG Signal Pathway
Abstract
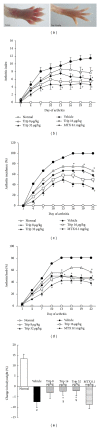
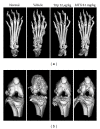
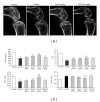
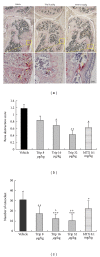
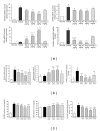
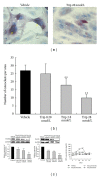
Focal bone destruction within inflamed joints is the most specific hallmark of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Our previous study indicated that the therapeutic efficiency of triptolide in RA may be due partially to its chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects. However, its roles in bone destruction are still unclear. In this study, our data firstly showed the therapeutic effects of triptolide on severity of arthritis and arthritis progression in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice. Then, by micro-CT quantification, triptolide treatment significantly increased bone mineral density, bone volume fraction, and trabecular thickness and decreased trabecular separation of inflamed joints. Interestingly, triptolide treatment could prevent the bone destruction by reducing the number of osteoclasts in inflamed joints, reducing the expression of receptor activator of NF- κ B (RANK) ligand (RANKL) and RANK, increasing the expression of osteoprotegerin (OPG), at both mRNA and protein levels, and decreasing the ratio of RANKL to OPG in sera and inflamed joints of CIA mice, which were further confirmed in the coculture system of human fibroblast-like synovial and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. These findings offer the convincing evidence for the first time that triptolide may attenuate RA partially by preventing the bone destruction and inhibit osteoclast formation by regulating RANKL/RANK/OPG signal pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Total Saponin from Anemone flaccida Fr. Schmidt Prevents Bone Destruction in Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis via Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis.Rejuvenation Res. 2015 Dec;18(6):528-42. doi: 10.1089/rej.2015.1688. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Rejuvenation Res. 2015. PMID: 26418168
-
Fengshi Qutong capsule ameliorates bone destruction of experimental rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jan 10;282:114602. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114602. Epub 2021 Sep 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34492323
-
Osteoprotegerin reduces osteoclast numbers and prevents bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis.Am J Pathol. 2002 Oct;161(4):1419-27. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64417-3. Am J Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12368214 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of receptor activator of NFkappaB ligand and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis.Bone. 2002 Feb;30(2):340-6. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(01)00682-2. Bone. 2002. PMID: 11856640 Review.
-
Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)/RANK/osteoprotegerin system in bone and other tissues (review).Mol Med Rep. 2015 May;11(5):3212-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3152. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25572286 Review.
Cited by
-
Osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand are involved in periodontitis-promoted vascular calcification.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jun 14;24(2):512. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11439. eCollection 2022 Aug. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35813311 Free PMC article.
-
Pathway of PPAR-gamma coactivators in thermogenesis: a pivotal traditional Chinese medicine-associated target for individualized treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 29;7(13):15885-900. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7419. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26895106 Free PMC article.
-
A systems biology-based investigation into the therapeutic effects of Gansui Banxia Tang on reversing the imbalanced network of hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2014 Feb 24;4:4154. doi: 10.1038/srep04154. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24561634 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of gene expression profiles in a rat adjuvant arthritis model suggests an effective role of triptolide via PI3K-AKT signaling.Exp Ther Med. 2019 May;17(5):3999-4006. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7425. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30988781 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F on treating rheumatoid arthritis explored by network pharmacology analysis and molecular docking.Open Med (Wars). 2024 May 30;19(1):20240967. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-0967. eCollection 2024. Open Med (Wars). 2024. PMID: 38841174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Böhler C, Radner H, Ernst M, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and falls: the influence of disease activity. Rheumatology. 2012;51:2051–2057. - PubMed
-
- Nanke Y, Yago T, Kotake S. The effects of disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs on osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2011;34:493–500. - PubMed
-
- Stolina M, Schett G, Dwyer D, et al. RANKL inhibition by osteoprotegerin prevents bone loss without affecting local or systemic inflammation parameters in two rat arthritis models: comparison with anti-TNFalpha or anti-IL-1 therapies. Arthritis Research & Therapy. 2009;11, article R187 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai YD, Yang FS, Xuan K, Bai YX, Wu BL. Inhibition of RANK/RANKL signal transduction pathway: a promising approach for osteoporosis treatment. Medical Hypotheses. 2008;71(2):256–258. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

