Towards polypharmacokinetics: pharmacokinetics of multicomponent drugs and herbal medicines using a metabolomics approach
- PMID: 23573155
- PMCID: PMC3612473
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/819147
Towards polypharmacokinetics: pharmacokinetics of multicomponent drugs and herbal medicines using a metabolomics approach
Abstract
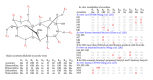
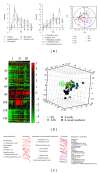
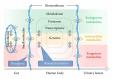
Determination of pharmacokinetics (PKs) of multicomponent pharmaceuticals and/or nutraceuticals (polypharmacokinetics, poly-PKs) is difficult due to the vast number of compounds present in natural products, their various concentrations across a wide range, complexity of their interactions, as well as their complex degradation dynamics in vivo. Metabolomics coupled with multivariate statistical tools that focus on the comprehensive analysis of small molecules in biofluids is a viable approach to address the challenges of poly-PK. This paper discusses recent advances in the characterization of poly-PK and the metabolism of multicomponent xenobiotic agents, such as compound drugs, dietary supplements, and herbal medicines, using metabolomics strategy. We propose a research framework that integrates the dynamic concentration profile of bioavailable xenobiotic molecules that result from in vivo absorption and hepatic and gut bacterial metabolism, as well as the human metabolic response profile. This framework will address the bottleneck problem in the pharmacological evaluation of multicomponent pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals, leading to the direct elucidation of the pharmacological and molecular mechanisms of these compounds.
Figures

References
-
- Blaylock RL. New developments in phytoprevention and treatment of cancer. The Journal of the American Nutraceutical Association. 1999;2:19–29.
-
- Hollander JM, Mechanick JI. Complementary and alternative medicine and the management of the metabolic syndrome. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. 2008;108(3):495–509. - PubMed
-
- Chan K. Progress in traditional Chinese medicine. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 1995;16(6):182–187. - PubMed
-
- Plumb GW, Garcia-Conesa MT, Kroon PA, Rhodes M, Ridley S, Williamson G. Metabolism of chlorogenic acid by human plasma, liver, intestine and gut microflora. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 1999;79(3):390–392.
-
- He SM, Chan E, Zhou SF. ADME properties of herbal medicines in humans: evidence, challenges andstrategies. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2011;17(4):357–407. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

