Zhen gan xi feng decoction, a traditional chinese herbal formula, for the treatment of essential hypertension: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 23573163
- PMCID: PMC3615628
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/982380
Zhen gan xi feng decoction, a traditional chinese herbal formula, for the treatment of essential hypertension: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
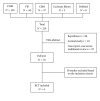
Objectives. To assess the clinical effectiveness and adverse effects of Zhen Gan Xi Feng Decoction (ZGXFD) for essential hypertension (EH). Methods. Five major electronic databases were searched up to August 2012 to retrieve any potential randomized controlled trials designed to evaluate the clinical effectiveness of ZGXFD for EH reported in any language, with main outcome measure as blood pressure (BP). Results. Six randomized trials were included. Methodological quality of the trials was evaluated as generally low. Four trials compared prescriptions based on ZGXFD with antihypertensive drugs. Meta-analysis showed that ZGXFD was more effective in BP control and TCM syndrome and symptom differentiation (TCM-SSD) scores than antihypertensive drugs. Two trials compared the combination of modified ZGXFD plus antihypertensive drugs with antihypertensive drugs. Meta-analysis showed that there is significant beneficial effect on TCM-SSD scores. However, no significant effect on BP was found. The safety of ZGXFD is still uncertain. Conclusions. ZGXFD appears to be effective in improving blood pressure and hypertension-related symptoms for EH. However, the evidence remains weak due to poor methodological quality of the included studies. More rigorous trials are warranted to support their clinical use.
Similar articles
-
Meta-analysis of the effectiveness of traditional Chinese herbal formula Zhen Wu Decoction for the treatment of hypertension.BMJ Open. 2015 Dec 11;5(12):e007291. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-007291. BMJ Open. 2015. PMID: 26656978 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese patent medicine liu wei di huang wan combined with antihypertensive drugs, a new integrative medicine therapy, for the treatment of essential hypertension: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:714805. doi: 10.1155/2012/714805. Epub 2012 Nov 11. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 23258998 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal medicine (Zhengan Xifeng Decoction) for essential hypertension protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Feb;98(6):e14292. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014292. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30732144 Free PMC article.
-
Banxia baizhu tianma decoction for essential hypertension: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:271462. doi: 10.1155/2012/271462. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 23320025 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine adjuvant therapy for severe pneumonia: evidence mapping of the randomized controlled trials, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 29;14:1227436. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1227436. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37841930 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evidence-based chinese medicine for hypertension.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:978398. doi: 10.1155/2013/978398. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23861720 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Dietary Components and Traditional Chinese Medicine on Hypertension: A Potential Role for Gut Microbiota.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Apr 20;2021:5563073. doi: 10.1155/2021/5563073. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33986817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quanduzhong capsules for the treatment of grade 1 hypertension patients with low-to-moderate risk: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1014410. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1014410. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36703729 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine Classic Herbal Formula Longdanxiegan Decoction for Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2018 May 8;9:466. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00466. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29867474 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and effectiveness of an herbal decoction (modified Saengmaeksan) in hypertensive patients: Protocol for a real-world prospective observational study.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 17;20(1):e0316276. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316276. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39823432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gu D, Reynolds K, Wu X, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in China. Hypertension. 2002;40(6):920–927. - PubMed
-
- Nabel EG. Cardiovascular disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;349:60–72. - PubMed
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. Seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42(6):1206–1252. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PM, Bloom B, Nahin RL. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults and children: United States, 2007. National Health Statistics Reports. 2009;10(12):1–23. - PubMed
-
- Su DJ, Li LF. Trends in the use of complementary and alternative medicine in the United States: 2002–2007. Journal of Health Care for the Poor and Underserved. 2011;22:295–309. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources