Optimization of contrast-to-tissue ratio by adaptation of transmitted ternary signal in ultrasound pulse inversion imaging
- PMID: 23573167
- PMCID: PMC3616357
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/297463
Optimization of contrast-to-tissue ratio by adaptation of transmitted ternary signal in ultrasound pulse inversion imaging
Abstract
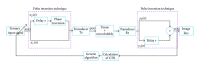
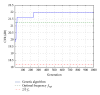
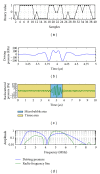
Ultrasound contrast imaging has provided more accurate medical diagnoses thanks to the development of innovating modalities like the pulse inversion imaging. However, this latter modality that improves the contrast-to-tissue ratio (CTR) is not optimal, since the frequency is manually chosen jointly with the probe. However, an optimal choice of this command is possible, but it requires precise information about the transducer and the medium which can be experimentally difficult to obtain, even inaccessible. It turns out that the optimization can become more complex by taking into account the kind of generators, since the generators of electrical signals in a conventional ultrasound scanner can be unipolar, bipolar, or tripolar. Our aim was to seek the ternary command which maximized the CTR. By combining a genetic algorithm and a closed loop, the system automatically proposed the optimal ternary command. In simulation, the gain compared with the usual ternary signal could reach about 3.9 dB. Another interesting finding was that, in contrast to what is generally accepted, the optimal command was not a fixed-frequency signal but had harmonic components.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimization of contrast resolution by genetic algorithm in ultrasound tissue harmonic imaging.Ultrasonics. 2016 Sep;71:231-244. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2016.06.022. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Ultrasonics. 2016. PMID: 27403642
-
Optimization of contrast-to-tissue ratio by frequency adaptation in pulse inversion imaging.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2012 Nov;59(11):2431-8. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2012.2475. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2012. PMID: 23192806
-
Ultrasound contrast imaging: influence of scatterer motion in multi-pulse techniques.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2013 Oct;60(10):2065-78. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2013.2797. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2013. PMID: 24081255
-
Broadband reduction of the second harmonic distortion during nonlinear ultrasound wave propagation.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010 Oct;36(10):1568-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2010.06.006. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20800962 Review.
-
Ultrasound contrast agents: basic principles.Eur J Radiol. 1998 May;27 Suppl 2:S157-60. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(98)00057-6. Eur J Radiol. 1998. PMID: 9652516 Review.
References
-
- Frinking PJA, Bouakaz A, Kirkhorn J, Ten Cate FJ, De Jong N. Ultrasound contrast imaging: current and new potential methods. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 2000;26(6):965–975. - PubMed
-
- Burns PN. Instrumentation for contrast echocardiography. Echocardiography. 2002;19(3):241–258. - PubMed
-
- Forsberg F, Shi WT, Goldberg BB. Subharmonic imaging of contrast agents. Ultrasonics. 2000;38(1):93–98. - PubMed
-
- Bouakaz A, Frigstad S, Ten Cate FJ, de Jong N. Super harmonic imaging: a new imaging technique for improved contrast detection. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 2002;28(1):59–68. - PubMed
-
- Tang MX, Mari JM, Wells PNT, Eckersley RJ. Attenuation correction in ultrasound contrast agent imaging: elementary theory and preliminary experimental evaluation. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 2008;34(12):1998–2008. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

