Review article: Fabrication of nanofluidic devices
- PMID: 23573176
- PMCID: PMC3612116
- DOI: 10.1063/1.4794973
Review article: Fabrication of nanofluidic devices
Abstract
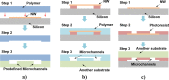
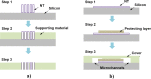
Thanks to its unique features at the nanoscale, nanofluidics, the study and application of fluid flow in nanochannels/nanopores with at least one characteristic size smaller than 100 nm, has enabled the occurrence of many interesting transport phenomena and has shown great potential in both bio- and energy-related fields. The unprecedented growth of this research field is apparently attributed to the rapid development of micro/nanofabrication techniques. In this review, we summarize recent activities and achievements of nanofabrication for nanofluidic devices, especially those reported in the past four years. Three major nanofabrication strategies, including nanolithography, microelectromechanical system based techniques, and methods using various nanomaterials, are introduced with specific fabrication approaches. Other unconventional fabrication attempts which utilize special polymer properties, various microfabrication failure mechanisms, and macro/microscale machining techniques are also presented. Based on these fabrication techniques, an inclusive guideline for materials and processes selection in the preparation of nanofluidic devices is provided. Finally, technical challenges along with possible opportunities in the present nanofabrication for nanofluidic study are discussed.
Figures
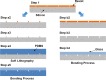
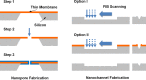
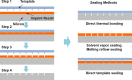

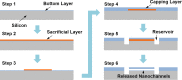


Similar articles
-
Fabrication of nanofluidic biochips with nanochannels for applications in DNA analysis.Small. 2012 Sep 24;8(18):2787-801. doi: 10.1002/smll.201200240. Epub 2012 Jul 9. Small. 2012. PMID: 22778064 Review.
-
Unconventional micro-/nanofabrication technologies for hybrid-scale lab-on-a-chip.Lab Chip. 2016 Nov 1;16(22):4296-4312. doi: 10.1039/c6lc01058j. Lab Chip. 2016. PMID: 27761529 Review.
-
Exploring Anomalous Fluid Behavior at the Nanoscale: Direct Visualization and Quantification via Nanofluidic Devices.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Feb 18;53(2):347-357. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00411. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 31922716
-
Nanofluidic devices and their applications.Anal Chem. 2008 Apr 1;80(7):2326-41. doi: 10.1021/ac702296u. Epub 2008 Mar 6. Anal Chem. 2008. PMID: 18321133
-
Scalable integration of nano-, and microfluidics with hybrid two-photon lithography.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2019 Sep 9;5:40. doi: 10.1038/s41378-019-0080-3. eCollection 2019. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2019. PMID: 31636930 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Standalone interferometry-based calibration of convex lens-induced confinement microscopy with nanoscale accuracy.Analyst. 2019 Apr 8;144(8):2628-2634. doi: 10.1039/c8an02300j. Analyst. 2019. PMID: 30839956 Free PMC article.
-
A Thorough Review of Emerging Technologies in Micro- and Nanochannel Fabrication: Limitations, Applications, and Comparison.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 Oct 21;15(10):1274. doi: 10.3390/mi15101274. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sample preconcentration utilizing nanofractures generated by junction gap breakdown assisted by self-assembled monolayer of gold nanoparticles.PLoS One. 2015 May 13;10(5):e0126641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126641. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25970592 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of all-transparent polymer-based and encapsulated nanofluidic devices using nano-indentation lithography.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2017 Mar 27;3:16084. doi: 10.1038/micronano.2016.84. eCollection 2017. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2017. PMID: 31057852 Free PMC article.
-
Ion diffusion coefficient measurements in nanochannels at various concentrations.Biomicrofluidics. 2014 Apr 30;8(2):024118. doi: 10.1063/1.4874215. eCollection 2014 Mar. Biomicrofluidics. 2014. PMID: 24803967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eijkel J. C. T. and v. d. Berg A., “Nanofluidics: What is it and what can we expect from it?” Microfluid. Nanofluid. 1(3), 249–267 (2005).10.1007/s10404-004-0012-9 - DOI
-
- Tas N. R., Mela P., Kramer T., Berenschot J. W., and van den Berg A., “Capillarity induced negative pressure of water plugs in nanochannels,” Nano Lett. 3(11), 1537–1540 (2003).10.1021/nl034676e - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
