Th17 immunity in children with allergic asthma and rhinitis: a pharmacological approach
- PMID: 23573194
- PMCID: PMC3616002
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058892
Th17 immunity in children with allergic asthma and rhinitis: a pharmacological approach
Abstract
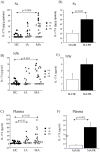
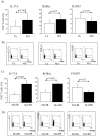
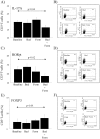
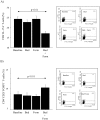
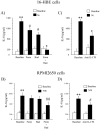
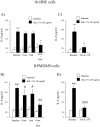
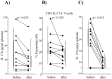
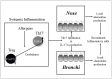
Th17 cells and IL-17A play a role in the development and progression of allergic diseases. We analyzed the IL-17A levels in sputum supernatants (Ss), nasal wash (NW) and plasma (P) from Healthy Controls (HC) and children with Asthma/Rhinitis. We tested the expression of IL-17A, RORγ(t) and FOXP3 in peripheral blood T-lymphocytes from intermittent and mild-moderate asthma. The effect of Budesonide and Formoterol was tested "in vitro" on IL-17A, RORγ(t) and FOXP3 expression in cultured T-lymphocytes from mild-moderate asthma/persistent rhinitis patients, and on nasal and bronchial epithelial cells stimulated with NW and Ss from mild-moderate asthma/persistent rhinitis. Further, the effect of 12 weeks of treatment with Budesonide and Formoterol was tested "in vivo" in T-lymphocytes from mild-moderate asthma/persistent rhinitis patients. IL-17A was increased in Ss, NW and P from children with mild-moderate asthma compared with intermittent and HC. In cultured T-lymphocytes IL-17A and RORγ(t) expression were higher in mild-moderate asthma/persistent rhinitis than in mild-moderate asthma/intermittent rhinitis, while FOXP3 was reduced. Budesonide with Formoterol reduced IL-17A and RORγ(t), while increased FOXP3 in cultured T-lymphocytes from mild-moderate asthma/persistent rhinitis, and reduced the IL-8 release mediated by IL-17A present in NW and Ss from mild-moderate asthma/persistent rhinitis in nasal and bronchial epithelial cells. Finally, Budesonide with Formoterol reduced IL-17A levels in P and Ss, CD4(+)IL-17A(+)T-cells, in naïve children with mild-moderate asthma/persistent rhinitis after 12 weeks of treatment. Th17 mediated immunity may be involved in the airway disease of children with allergic asthma and allergic rhinitis. Budesonide with Formoterol might be a useful tool for its therapeutic control.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased IL-17A secreting CD4+ T cells, serum IL-17 levels and exhaled nitric oxide are correlated with childhood asthma severity.Clin Exp Allergy. 2013 Sep;43(9):1018-26. doi: 10.1111/cea.12119. Clin Exp Allergy. 2013. PMID: 23957337
-
Fast beneficial systemic anti-inflammatory effects of inhaled budesonide and formoterol on circulating lymphocytes in asthma.Respirology. 2013 Jul;18(5):840-7. doi: 10.1111/resp.12104. Respirology. 2013. PMID: 23617551 Clinical Trial.
-
[The expression of Treg/Th17 cells related transcription factors and cytokines in PBMCs and plasma in patients with allergic rhinitis].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012 Mar;26(5):209-11. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2012.05.009. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22667131 Chinese.
-
Budesonide/formoterol pressurized metered-dose inhaler for patients with persistent asthma.Allergy Asthma Proc. 2010 May-Jun;31(3):190-202. doi: 10.2500/aap.2010.31.3356. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2010. PMID: 20482961 Review.
-
Budesonide/formoterol: a review of its use as maintenance and reliever inhalation therapy in asthma.Drugs. 2007;67(16):2407-31. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200767160-00007. Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17983258 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of IL-17 in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Rhinitis Model.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017 Mar;9(2):169-176. doi: 10.4168/aair.2017.9.2.169. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 28102062 Free PMC article.
-
An association analysis to identify genetic variants linked to asthma and rhino-conjunctivitis in a cohort of Sicilian children.Ital J Pediatr. 2019 Jan 15;45(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13052-019-0603-4. Ital J Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 30646946 Free PMC article.
-
TH17 cells and corticosteroid insensitivity in severe asthma.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022 Feb;149(2):467-479. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.12.769. Epub 2021 Dec 23. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34953791 Free PMC article.
-
TH17 Cell Frequency in Peripheral Blood Is Elevated in Overweight Children without Chronic Inflammatory Diseases.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 16;8:1543. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01543. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29201026 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Administration of Calea pinnatifida Inhibits Inflammation Induced by Carrageenan in a Murine Model of Pulmonary Neutrophilia.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Jan 25;2020:4620251. doi: 10.1155/2020/4620251. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32410853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bourdin A, Gras D, Vachier I, Chanez P (2009) Upper airway x 1: allergic rhinitis and asthma: united disease through epithelial cells Thorax. 64: 999–1004. - PubMed
-
- Oboki K, Ohno T, Saito H, Nakae S (2008) Th17 and allergy. Allergol Int. 57: 121–34. - PubMed
-
- Robinson DS (2009) Regulatory T cells and asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 39: 1314–23. - PubMed
-
- Alcorn JF, Crowe CR, Kolls JK (2010) TH17 cells in asthma and COPD. Annu Rev Physiol. 72: 495–516. - PubMed
-
- Molet S, Hamid Q, Davoine F, Nutku E, Taha R, et al. (2001) IL-17 is increased in asthmatic airways and induces human bronchial fibroblasts to produce cytokines. Allergy Clin Immunol 108: 430–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

