Rasagiline ameliorates olfactory deficits in an alpha-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 23573275
- PMCID: PMC3616111
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060691
Rasagiline ameliorates olfactory deficits in an alpha-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
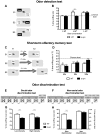
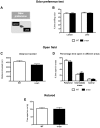
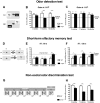
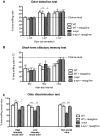
Impaired olfaction is an early pre-motor symptom of Parkinson's disease. The neuropathology underlying olfactory dysfunction in Parkinson's disease is unknown, however α-synuclein accumulation/aggregation and altered neurogenesis might play a role. We characterized olfactory deficits in a transgenic mouse model of Parkinson's disease expressing human wild-type α-synuclein under the control of the mouse α-synuclein promoter. Preliminary clinical observations suggest that rasagiline, a monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor, improves olfaction in Parkinson's disease. We therefore examined whether rasagiline ameliorates olfactory deficits in this Parkinson's disease model and investigated the role of olfactory bulb neurogenesis. α-Synuclein mice were progressively impaired in their ability to detect odors, to discriminate between odors, and exhibited alterations in short-term olfactory memory. Rasagiline treatment rescued odor detection and odor discrimination abilities. However, rasagiline did not affect short-term olfactory memory. Finally, olfactory changes were not coupled to alterations in olfactory bulb neurogenesis. We conclude that rasagiline reverses select olfactory deficits in a transgenic mouse model of Parkinson's disease. The findings correlate with preliminary clinical observations suggesting that rasagiline ameliorates olfactory deficits in Parkinson's disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
α-Synuclein Pathology and Reduced Neurogenesis in the Olfactory System Affect Olfaction in a Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease.J Neurosci. 2023 Feb 8;43(6):1051-1071. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1526-22.2022. Epub 2023 Jan 3. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36596700 Free PMC article.
-
Rasagiline and selegiline modulate mitochondrial homeostasis, intervene apoptosis system and mitigate α-synuclein cytotoxicity in disease-modifying therapy for Parkinson's disease.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2020 Feb;127(2):131-147. doi: 10.1007/s00702-020-02150-w. Epub 2020 Jan 28. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2020. PMID: 31993732 Review.
-
Reduced cerebral blood flow in an α-synuclein transgenic mouse model of Parkinson's disease.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020 Dec;40(12):2441-2453. doi: 10.1177/0271678X19895432. Epub 2019 Dec 19. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020. PMID: 31856640 Free PMC article.
-
Early Parkinson's disease patients on rasagiline present with better odor discrimination.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015 Nov;122(11):1541-6. doi: 10.1007/s00702-015-1433-1. Epub 2015 Jul 30. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015. PMID: 26224038
-
Comprehensive review of rasagiline, a second-generation monoamine oxidase inhibitor, for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.Clin Ther. 2007 Sep;29(9):1825-49. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.09.021. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18035186 Review.
Cited by
-
Mannose 6-Phosphate Receptor Is Reduced in -Synuclein Overexpressing Models of Parkinsons Disease.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 10;11(8):e0160501. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160501. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27509067 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT2A Receptor Binding in the Frontal Cortex of Parkinson's Disease Patients and Alpha-Synuclein Overexpressing Mice: A Postmortem Study.Parkinsons Dis. 2016;2016:3682936. doi: 10.1155/2016/3682936. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Parkinsons Dis. 2016. PMID: 27579212 Free PMC article.
-
ATH434 Rescues Pre-motor Hyposmia in a Mouse Model of Parkinsonism.Neurotherapeutics. 2022 Oct;19(6):1966-1975. doi: 10.1007/s13311-022-01300-0. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Neurotherapeutics. 2022. PMID: 36175781 Free PMC article.
-
Neural and vascular contributions to sensory impairments in a human alpha-synuclein transgenic mouse model of Parkinson's disease.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025 May 7:271678X251338952. doi: 10.1177/0271678X251338952. Online ahead of print. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025. PMID: 40334688 Free PMC article.
-
Non-motor features of Parkinson disease.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017 Jul;18(7):435-450. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.62. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28592904 Review.
References
-
- Chaudhuri KR, Naidu Y (2008) Early Parkinson's disease and non-motor issues. J Neurol 255: S33–38. - PubMed
-
- Kranick SM, Duda JE (2008) Olfactory dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Neurosignals 16: 35–40. - PubMed
-
- Haehner A, Boesveldt S, Berendse HW, Mackay-Sim A, Fleischmann J, et al. (2009) Prevalence of smell loss in Parkinson's disease--a multicenter study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15: 490–494. - PubMed
-
- Ross GW, Petrovitch H, Abbott RD, Tanner CM, Popper J, et al. (2008) Association of olfactory dysfunction with risk for future Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 63: 167–173. - PubMed
-
- Haehner A, Hummel T, Reichmann H (2010) Olfactory Function in Parkinson's Disease. Eur Neurol Rev 5: 26–29.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

