Dexamethasone inhibits repair of human airway epithelial cells mediated by glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ)
- PMID: 23573276
- PMCID: PMC3615997
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060705
Dexamethasone inhibits repair of human airway epithelial cells mediated by glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ)
Abstract
Background: Glucocorticoids (GCs) are a first-line treatment for asthma for their anti-inflammatory effects, but they also hinder the repair of airway epithelial injury. The anti-inflammatory protein GC-induced leucine zipper (GILZ) is reported to inhibit the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway, which promotes the repair of airway epithelial cells around the damaged areas. We investigated whether the inhibition of airway epithelial repair imposed by the GC dexamethasone (DEX) is mediated by GILZ.
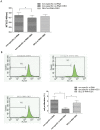
Methods: We tested the effect of DEX on the expressions of GILZ mRNA and GILZ protein and the MAPK-ERK signaling pathway in human airway epithelial cells, via RT-PCR and Western blot. We further evaluated the role of GILZ in mediating the effect of DEX on the MAPK-ERK signaling pathway and in airway epithelium repair by utilizing small-interfering RNAs, MTT, CFSE labeling, wound-healing and cell migration assays.
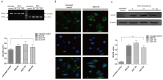
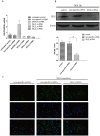
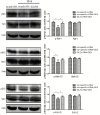
Results: DEX increased GILZ mRNA and GILZ protein levels in a human airway epithelial cell line. Furthermore, DEX inhibited the phosphorylation of Raf-1, Mek1/2, Erk1/2 (components of the MAPK-ERK signaling pathway), proliferation and migration. However, the inhibitory effect of DEX was mitigated in cells when the GILZ gene was silenced.
Conclusions: The inhibition of epithelial injury repair by DEX is mediated in part by activation of GILZ, which suppressed activation of the MAPK-ERK signaling pathway, proliferation and migration. Our study implicates the involvement of DEX in this process, and furthers our understanding of the dual role of GCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vitamin A maintains the airway epithelium in a murine model of asthma by suppressing glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper.Clin Exp Allergy. 2016 Jun;46(6):848-60. doi: 10.1111/cea.12646. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016. PMID: 26399569
-
MiR-222-3p ameliorates glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of airway epithelial cell repair through down-regulating GILZ expression.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2020 Aug;40(4):301-312. doi: 10.1080/10799893.2020.1742739. Epub 2020 Mar 21. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2020. PMID: 32202184
-
Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper inhibits the Raf-extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway by binding to Raf-1.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Nov;22(22):7929-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.22.7929-7941.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12391160 Free PMC article.
-
Implicating the Role of GILZ in Glucocorticoid Modulation of T-Cell Activation.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 7;10:1823. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01823. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31440237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ): a new important mediator of glucocorticoid action.FASEB J. 2009 Nov;23(11):3649-58. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-134684. Epub 2009 Jun 30. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19567371 Review.
Cited by
-
Antileukotriene reverts the early effects of inflammatory response of distal parenchyma in experimental chronic allergic inflammation.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:523761. doi: 10.1155/2013/523761. Epub 2013 Sep 15. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24151607 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase contributes to the repair of human airway epithelial cells inhibited by dexamethasone via affecting the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jul;16(1):282-290. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6163. Epub 2018 May 14. Exp Ther Med. 2018. Retraction in: Exp Ther Med. 2024 Feb 19;27(4):144. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12432. PMID: 29896251 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
GILZ as a Regulator of Cell Fate and Inflammation.Cells. 2021 Dec 30;11(1):122. doi: 10.3390/cells11010122. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of miR‑375 reverses the effects of dexamethasone on the viability, migration, invasion and apoptosis of human airway epithelial cells by targeting DUSP6.Int J Mol Med. 2022 Mar;49(3):26. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5081. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35014672 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Dexamethasone-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles on Oral Mucositis Induced by 5-Fluorouracil.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jan 4;13(1):53. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13010053. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33406583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tam A, Wadsworth S, Dorscheid D, Man SF, Sin DD (2011) The airway epithelium: more than just a structural barrier. Ther Adv Respir Dis 5: 255–273. - PubMed
-
- Holgate ST (2008) The airway epithelium is central to the pathogenesis of asthma. Allergol Int 57: 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Barbato A, Turato G, Baraldo S, Bazzan E, Calabrese F, et al. (2006) Epithelial damage and angiogenesis in the airways of children with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174: 975–981. - PubMed
-
- Dorscheid DR, Wojcik KR, Sun S, Marroquin B, White SR (2001) Apoptosis of airway epithelial cells induced by corticosteroids. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164: 1939–1947. - PubMed
-
- Spangler DL (2012) The role of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma treatment: a health economic perspective. Am J Manag Care 18: S35–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

