Generation of mast cells from mouse fetus: analysis of differentiation and functionality, and transcriptome profiling using next generation sequencer
- PMID: 23573287
- PMCID: PMC3616098
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060837
Generation of mast cells from mouse fetus: analysis of differentiation and functionality, and transcriptome profiling using next generation sequencer
Abstract
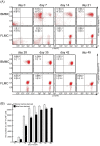
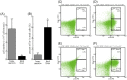
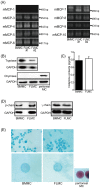
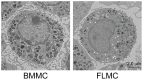
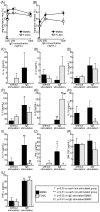
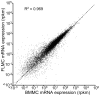
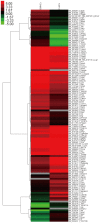
While gene knockout technology can reveal the roles of proteins in cellular functions, including in mast cells, fetal death due to gene manipulation frequently interrupts experimental analysis. We generated mast cells from mouse fetal liver (FLMC), and compared the fundamental functions of FLMC with those of bone marrow-derived mouse mast cells (BMMC). Under electron microscopy, numerous small and electron-dense granules were observed in FLMC. In FLMC, the expression levels of a subunit of the FcεRI receptor and degranulation by IgE cross-linking were comparable with BMMC. By flow cytometry we observed surface expression of c-Kit prior to that of FcεRI on FLMC, although on BMMC the expression of c-Kit came after FcεRI. The surface expression levels of Sca-1 and c-Kit, a marker of putative mast cell precursors, were slightly different between bone marrow cells and fetal liver cells, suggesting that differentiation stage or cell type are not necessarily equivalent between both lineages. Moreover, this indicates that phenotypically similar mast cells may not have undergone an identical process of differentiation. By comprehensive analysis using the next generation sequencer, the same frequency of gene expression was observed for 98.6% of all transcripts in both cell types. These results indicate that FLMC could represent a new and useful tool for exploring mast cell differentiation, and may help to elucidate the roles of individual proteins in the function of mast cells where gene manipulation can induce embryonic lethality in the mid to late stages of pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kulka M (2009) The potential of natural products as effective treatments for allergic inflammation: implications for allergic rhinitis. Curr Top Med Chem 9: 1611–1624. - PubMed
-
- Kubo Y, Fukuishi N, Yoshioka M, Kawasoe Y, Iriguchi S, et al. (2007) Bacterial components regulate the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 on human mast cells. Inflamm Res 56: 70–75. - PubMed
-
- Fukuishi N, Metcalfe DD, Kulka M (2004) Sounding the alarm in infection; Mast cell counter-attack. J World Allefgy Organization 16: 70–74.
-
- Yoshioka M, Fukuishi N, Iriguchi S, Ohsaki K, Yamanobe H, et al. (2007) Lipoteichoic acid downregulates FcepsilonRI expression on human mast cells through Toll-like receptor 2. J Allergy Clin Immunol 120: 452–461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

