WWP1 E3 ligase targets LATS1 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 23573293
- PMCID: PMC3616014
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061027
WWP1 E3 ligase targets LATS1 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation in breast cancer cells
Abstract
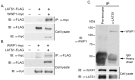
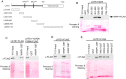
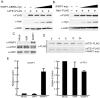
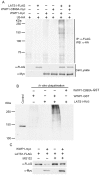
The Large Tumor Suppressor 1 (LATS1) is a serine/threonine kinase and tumor suppressor found down-regulated in various human cancers. LATS1 has recently been identified as a central player of the emerging Hippo signaling pathway, which plays important roles in organ size control, tumorigenesis, and stem cell differentiation and renewal, etc. Although mounting evidence supports a role of LATS1 in tumor suppression and tumorigenesis, how LATS1 is regulated at the molecular level is not fully understood. Recently several positive regulators of LATS1 (Mst1/2, MOB1, Kibra, etc) have been identified but how LATS1 is negatively regulated is still largely unknown. We have recently identified Itch, a member of the NEDD4-like family E3 ubiquitin ligases, as a novel negative regulator of LATS1. However, whether other ubiquitin ligases modulate LATS1 stability and function is unclear. By screening many E3 ligases of the NEDD4-like family using over-expression and short-interference RNA knockdown approaches, we have identified WWP1 E3 ligase as another novel negative regulator of LATS1. We have provided in vitro and in vivo evidence that WWP1 is essential for LATS1 stability and negatively regulate LATS1 by promoting LATS1 degradation through polyubiquitination and the 26S proteasome pathway. Importantly, we also showed that degradation of LATS1 is critical in mediating WWP1-induced increased cell proliferation in breast cancer cells. Since WWP1 is an oncogene and LATS1 is a tumor suppressor gene in breast cancer, our studies provide a promising therapeutic strategy in which developed drugs targeting WWP1 cause activation of LATS1 in suppressing breast cancer cell growth.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Visser S, Yang X (2010) LATS tumor suppressor: A new governor of cellular homeostasis. Cell Cycle 9: 3892–3903. - PubMed
-
- Yang X, Yu K, Hao Y, Li DM, Stewart R, et al. (2004) LATS1 tumour suppressor affects cytokinesis by inhibiting LIMK1. Nature Cell Biology 6: 609–617. - PubMed
-
- Yang X, Li DM, Chen W, Xu T (2001) Human homologue of drosophila lats, LATS1, negatively regulate growth by inducing G(2)/M arrest or apoptosis. Oncogene 20: 6516–23. - PubMed
-
- Lai D, Ho KC, Hao Y, Yang X (2011) Taxol resistance in breast cancer cells is mediated by the hippo pathway component TAZ and its downstream transcriptional targets Cyr61 and CTGF. Cancer Research 71: 2728–2738. - PubMed
-
- Tremblay AM, Camargo FD (2012) Hippo signaling in mammalian stem cells. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology 23: 818–826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

