EGFR-targeted granzyme B expressed in NK cells enhances natural cytotoxicity and mediates specific killing of tumor cells
- PMID: 23573299
- PMCID: PMC3616035
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061267
EGFR-targeted granzyme B expressed in NK cells enhances natural cytotoxicity and mediates specific killing of tumor cells
Abstract
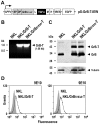
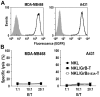
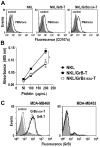
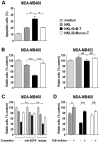
Natural killer (NK) cells are highly specialized effectors of the innate immune system that hold promise for adoptive cancer immunotherapy. Their cell killing activity is primarily mediated by the pro-apoptotic serine protease granzyme B (GrB), which enters targets cells with the help of the pore-forming protein perforin. We investigated expression of a chimeric GrB fusion protein in NK cells as a means to augment their antitumoral activity. For selective targeting to tumor cells, we fused the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) peptide ligand transforming growth factor α (TGFα) to human pre-pro-GrB. Established human NKL natural killer cells transduced with a lentiviral vector expressed this GrB-TGFα (GrB-T) molecule in amounts comparable to endogenous wildtype GrB. Activation of the genetically modified NK cells by cognate target cells resulted in the release of GrB-T together with endogenous granzymes and perforin, which augmented the effector cells' natural cytotoxicity against NK-sensitive tumor cells. Likewise, GrB-T was released into the extracellular space upon induction of degranulation with PMA and ionomycin. Secreted GrB-T fusion protein displayed specific binding to EGFR-overexpressing tumor cells, enzymatic activity, and selective target cell killing in the presence of an endosomolytic activity. Our data demonstrate that ectopic expression of a targeted GrB fusion protein in NK cells is feasible and can enhance antitumoral activity of the effector cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Smyth MJ, Hayakawa Y, Takeda K, Yagita H (2002) New aspects of natural-killer-cell surveillance and therapy of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 850–861. - PubMed
-
- Bromley SK, Burack WR, Johnson KG, Somersalo K, Sims TN, et al. (2001) The immunological synapse. Annu Rev Immunol 19: 375–396. - PubMed
-
- Cullen SP, Brunet M, Martin SJ (2010) Granzymes in cancer and immunity. Cell Death Differ 17: 616–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

