Human fetal ductal plate revisited: II. MUC1, MUC5AC, and MUC6 are expressed in human fetal ductal plate and MUC1 is expressed also in remodeling ductal plate, remodeled ductal plate and mature bile ducts of human fetal livers
- PMID: 23573304
- PMCID: PMC3606847
Human fetal ductal plate revisited: II. MUC1, MUC5AC, and MUC6 are expressed in human fetal ductal plate and MUC1 is expressed also in remodeling ductal plate, remodeled ductal plate and mature bile ducts of human fetal livers
Abstract
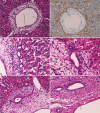
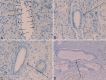
Mucins are high-molecular-weight glycoproteins, which are heavily decorated with a large number of O-linked oligosaccharides and a few N-glycan chains, linked to a protein backbone. The protein backbone is called mucin core protein or MUC apomucins. MUC expression is down-regulated or up-regulated in malignant neoplasms. These alterations of MUC apomucins, which are regulated by MUC genes, are associated with carcinogenesis and malignant potentials of cancers. MUC expression during human fetal intrahepatic bile duct (IBD) development has been studied only once, and there has been only one histochemical study of mucins in human fetal IBD development. The author herein immunohistochemically investigated the expression of MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC6, and histochemically investigated carbohydrate component of mucins in human fetal cholangiocytes with the use of 32 human fetal livers of various gestational ages. MUC1 is a transmembranous apomucin, while MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6 are secretory apomucins. Under normal conditions, MUC1 (polymorphic epithelial mucin) is present mainly in the pancreatic epithelium. MUC2 (goblet cell mucin) is mainly located in goblet cells. MUC5AC (gastric foveolar mucin) and MUC6 (pyloric gland-type mucin) are located in the stomach. In the present study, the processes of the human IBD development could be categorized into four stages; ductal plate (DP), remodeling DP, remodeled DP, and mature IBDs. The author identified that MUC1 was present in ductal plate (DP), remodeling DP, remodeled DP, and mature IBD in human fetal livers. MUC5AC and MUC6 were present only in the DP. MUC5AC and MUC6 were absent in remodeling DP, remodeled DP, and mature IBD in human fetal livers. No expression of MUC2 was seen throughout the fetal IBD development. Histochemically, no carbohydrate component of mucins were seen in the remodeling DP and remodeled DP, while neutral and acidic mucins (carboxylated and sulfated mucins) were seen in mature IBD in human fetal livers. The DP showed frequently neutral mucins and less frequently acidic mucins (carboxylated and sulfated mucins residues). These findings suggest that the DP cells have MUC1, MUC5AC and MUC6, and that remodeling DP, remodeled DP, and mature IBDs have MUC1, but not MUC5AC and MUC6. The presence of neutral and acidic carbohydrates in DP suggests that these carbohydrates of mucin are attached to the MUC5AC and MUC6 mucin core proteins. Although the implications are unclear, the expression of these MUC apomucins and their carbohydrate residues are associated with normal development of IBDs in human fetal livers.
Keywords: Ductal plate; MUC apomucins; histochemistry; human fetal liver; immunohistochemistry; intrahepatic bile duct development; mucins.
Figures




Similar articles
-
An immunohistochemical study of primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the stomach and colorectum: II. Expression of MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC6 in normal mucosa and in 42 cases.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6(4):613-21. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23573307 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of mucins (MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6) in mucinous carcinoma of the breast: comparison with invasive ductal carcinoma.Histopathology. 2003 Jan;42(1):26-36. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2003.01530.x. Histopathology. 2003. PMID: 12493022
-
Expression of mucin antigens in human cancers and its relationship with malignancy potential.Pathol Int. 1997 Dec;47(12):813-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1997.tb03713.x. Pathol Int. 1997. PMID: 9503463 Review.
-
Intestinal metaplasia of human stomach displays distinct patterns of mucin (MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC6) expression.Cancer Res. 1999 Mar 1;59(5):1003-7. Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10070955
-
Significance of mucin expression in pancreatobiliary neoplasms.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010 Mar;17(2):108-24. doi: 10.1007/s00534-009-0174-7. Epub 2009 Sep 29. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010. PMID: 19787286 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatobiliary cystadenocarcinoma of the liver with features of ductal plate malformations.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2015 Jun;46(2):197-200. doi: 10.1007/s12029-015-9688-1. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25656967 No abstract available.
-
Mucins: the Old, the New and the Promising Factors in Hepatobiliary Carcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 14;20(6):1288. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061288. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30875782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging in ductal plate malformations.Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2017 Jan-Mar;27(1):6-12. doi: 10.4103/0971-3026.202966. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28515578 Free PMC article.
-
Two-stage Cox-nnet: biologically interpretable neural-network model for prognosis prediction and its application in liver cancer survival using histopathology and transcriptomic data.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2021 Mar 22;3(1):lqab015. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqab015. eCollection 2021 Mar. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33778491 Free PMC article.
-
Human ductal plate and its derivatives express antigens of cholangiocellular, hepatocellular, hepatic stellate/progenitor cell, stem cell, and neuroendocrine lineages, and proliferative antigens.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 May;242(9):907-917. doi: 10.1177/1535370216644684. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 27075931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Terada T, Nakanuma Y. Development of human intrahepatic peribiliary glands: Histological, keratin immunohistochemical and mucus histochemical analyses. Lab Invest. 1993;68:261–269. - PubMed
-
- Terada T, Nakanuma Y. Profiles of expression of carbohydrate chain structures during human intrahepatic bile duct development and maturation: a lectin-histochemical and immunohistochemical study. Hepatology. 1994;20:388–397. - PubMed
-
- Terada T, Kitamura Y, Nakanuma Y. Normal and abnormal development of the intrahepatic biliary system: A review. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1997;181:19–32. - PubMed
-
- Terada T, Ashida K, Kitamura Y, Matsunaga Y, Takashima K, Kato M, Ohta T. Expression of E-cadherin, alpha-catenin and beta-catenin during human intrahepatic bile duct development. J Hepatol. 1998;28:263–269. - PubMed
-
- Terada T. Differentiation of intrahepatic peribiliary glands and pancreatic acinar cells from the remodeling ductal plate in human fetuses. Hepatology. 2012;56:2004–2005. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
