The rising burden of diabetes and hypertension in southeast asian and african regions: need for effective strategies for prevention and control in primary health care settings
- PMID: 23573413
- PMCID: PMC3612479
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/409083
The rising burden of diabetes and hypertension in southeast asian and african regions: need for effective strategies for prevention and control in primary health care settings
Abstract
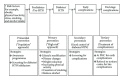
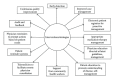
Aim. To review the available literature on burden of diabetes mellitus (DM) and hypertension (HTN) and its coexistence in Southeast Asian (SEA) and the African (AFR) regions and to suggest strategies to improve DM and HTN prevention and control in primary health care (PHC) in the two regions. Methods. A systematic review of the papers published on DM, HTN, and prevention/control of chronic diseases in SEA and AFR regions between 1980 and December 2012 was included. Results. In the year 2011, SEA region had the second largest number of people with DM (71.4 million), while the AFR region had the smallest number (14.7 million). Screening studies identified high proportions (>50%) of individuals with previously undiagnosed HTN and DM in both of the SEA and AFR regions. Studies from both regions have shown that DM and HTN coexist in type 2 DM ranging from 20.6% in India to 78.4% in Thailand in the SEA region and ranging from 9.7% in Nigeria to 70.4% in Morocco in the AFR region. There is evidence that by lifestyle modification both DM and HTN can be prevented. Conclusion. To meet the twin challenge of DM and HTN in developing countries, PHCs will have to be strengthened with a concerted and multipronged effort to provide promotive, preventive, curative, and rehabilitative services.
Figures
References
-
- King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995–2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(9):1414–1431. - PubMed
-
- Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lu Y, et al. National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2·7 million participants. The Lancet. 2011;378(9785):31–40. - PubMed
-
- Unwin N, Whiting D, Guariguata L, Ghyoot G, Gan D, editors. Diabetes Atlas. 5th edition. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2011.
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. The seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure: the JNC 7 report. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 2003;289(19):2560–2572. - PubMed
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. The Lancet. 2005;365(9455):217–223. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources