Progress in immune-based therapies for type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 23574316
- PMCID: PMC3628322
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12085
Progress in immune-based therapies for type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Immune-based therapies that prevent type 1 diabetes or preserve metabolic function remaining at diagnosis have become a major objective for funding agencies and international trial consortia, and receive backing from notable patient advocate groups. The development of immune-based therapeutic strategies in this arena requires a careful balancing of the risks of the therapy against the potential benefits, because many individuals are diagnosed or identified as being at increased risk of disease in early childhood, a period when manipulation of the developing immune system should be undertaken with caution. In addition, a therapy exists (daily insulin injection) that is life-saving in the acute stages of disease and can be used effectively over a lifetime as maintenance. Conversely, the disease is increasing in incidence; is peaking in ever-younger age groups; carries significant risk of increased morbidity and early mortality; and remains difficult to manage effectively in many settings. With these issues in mind, in this article we review progress towards immune-based strategies for this chronic autoimmune disease.
© 2013 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
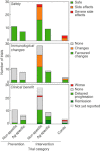

References
-
- Herold KC, Hagopian W, Auger JA, et al. Anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody in new-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1692–1698. - PubMed
-
- Keymeulen B, Vandemeulebroucke E, Ziegler AG, et al. Insulin needs after CD3-antibody therapy in new-onset type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2598–2608. - PubMed
-
- Roep BO, Peakman M. Surrogate end points in the design of immunotherapy trials: emerging lessons from type 1 diabetes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:145–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

