The importance of first pass success when performing orotracheal intubation in the emergency department
- PMID: 23574475
- PMCID: PMC4530518
- DOI: 10.1111/acem.12055
The importance of first pass success when performing orotracheal intubation in the emergency department
Abstract
Objectives: The goal of this study was to determine the association of first pass success with the incidence of adverse events (AEs) during emergency department (ED) intubations.
Methods: This was a retrospective analysis of prospectively collected continuous quality improvement data based on orotracheal intubations performed in an academic ED over a 4-year period. Following each intubation, the operator completed a data form regarding multiple aspects of the intubation, including patient and operator characteristics, method of intubation, device used, the number of attempts required, and AEs. Numerous AEs were tracked and included events such as witnessed aspiration, oxygen desaturation, esophageal intubation, hypotension, dysrhythmia, and cardiac arrest. Multivariable logistic regression was used to assess the relationship between the primary predictor variable of interest, first pass success, and the outcome variable, the presence of one or more AEs, after controlling for various other potential risk factors and confounders.
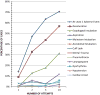
Results: Over the 4-year study period, there were 1,828 orotracheal intubations. If the intubation was successful on the first attempt, the incidence of one or more AEs was 14.2% (95% confidence interval [CI] = 12.4% to 16.2%). In cases requiring two attempts, the incidence of one or more AEs was 47.2% (95% CI = 41.8% to 52.7%); in cases requiring three attempts, the incidence of one or more AEs was 63.6% (95% CI = 53.7% to 72.6%); and in cases requiring four or more attempts, the incidence of one or more AEs was 70.6% (95% CI = 56.2.3% to 82.5%). Multivariable logistic regression showed that more than one attempt at tracheal intubation was a significant predictor of one or more AEs (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 7.52, 95% CI = 5.86 to 9.63).
Conclusions: When performing orotracheal intubation in the ED, first pass success is associated with a relatively small incidence of AEs. As the number of attempts increases, the incidence of AEs increases substantially.
© 2013 by the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine.
Figures
Comment in
-
In reply.Acad Emerg Med. 2013 Sep;20(9):966. doi: 10.1111/acem.12198. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Acad Emerg Med. 2013. PMID: 23981050 No abstract available.
-
Chicken or egg? Risks of misattribution of cause-effect relationships in studies of association.Acad Emerg Med. 2013 Sep;20(9):965. doi: 10.1111/acem.12199. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Acad Emerg Med. 2013. PMID: 23981076 No abstract available.
References
-
- Martin LD, Mhyre JM, Shanks AM, Tremper KK, Kheterpal S. 3,423 emergency tracheal intubations at a university hospital: airway outcomes and complications. Anesthesiology. 2011;114:42–8. - PubMed
-
- Mort TC. Emergency tracheal intubation: complications associated with repeated laryngoscopic attempts. Anesth Analg. 2004;99:607–13. - PubMed
-
- Mort TC. The incidence and risk factors for cardiac arrest during emergency tracheal intubation: a justification for incorporating the ASA guidelines in the remote location. J Clin Anesth. 2004;16:508–16. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz DE, Matthay MA, Cohen NH. Death and other complications of emergency airway management in critically ill adults. A prospective investigation of 297 tracheal intubations. Anesthesiology. 1995;82:367–6. - PubMed
-
- Tayal VS, Riggs RW, Marx JA, Tomaszewski CA, Schneider RE. Rapid-sequence intubation at an emergency medicine residency: success rate and adverse events during a two-year period. Acad Emerg Med. 1999;6:31–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials