Analysis of a gene co-expression network establishes robust association between Col5a2 and ischemic heart disease
- PMID: 23574622
- PMCID: PMC3637268
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-6-13
Analysis of a gene co-expression network establishes robust association between Col5a2 and ischemic heart disease
Abstract
Background: This study aims to expand knowledge of the complex process of myocardial infarction (MI) through the application of a systems-based approach.
Methods: We generated a gene co-expression network from microarray data originating from a mouse model of MI. We characterized it on the basis of connectivity patterns and independent biological information. The potential clinical novelty and relevance of top predictions were assessed in the context of disease classification models. Models were validated using independent gene expression data from mouse and human samples.
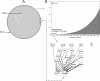
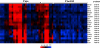
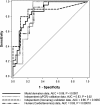
Results: The gene co-expression network consisted of 178 genes and 7298 associations. The network was dissected into statistically and biologically meaningful communities of highly interconnected and co-expressed genes. Among the most significant communities, one was distinctly associated with molecular events underlying heart repair after MI (P < 0.05). Col5a2, a gene previously not specifically linked to MI response but responsible for the classic type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, was found to have many and strong co-expression associations within this community (11 connections with ρ > 0.85). To validate the potential clinical application of this discovery, we tested its disease discriminatory capacity on independently generated MI datasets from mice and humans. High classification accuracy and concordance was achieved across these evaluations with areas under the receiving operating characteristic curve above 0.8.
Conclusion: Network-based approaches can enable the discovery of clinically-interesting predictive insights that are accurate and robust. Col5a2 shows predictive potential in MI, and in principle may represent a novel candidate marker for the identification and treatment of ischemic cardiovascular disease.
Figures

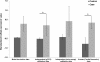
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

