Ceruminal diffusion activities and ceruminolytic characteristics of otic preparations - an in-vitro study
- PMID: 23574753
- PMCID: PMC3641987
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-6148-9-70
Ceruminal diffusion activities and ceruminolytic characteristics of otic preparations - an in-vitro study
Abstract
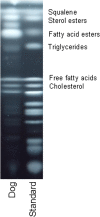
Background: An in-vitro setup was established in order to determine a) the diffusion activities of eight otic preparations (Aurizon®, Eas Otic®, Epi Otic®, Otifree®, Otomax®, Panolog®, Posatex®, Surolan®) through synthetic cerumen, and b) the ceruminolytic capacity and impregnation effects of these products. The main lipid classes of canine cerumen produced with moderate, non-purulent otitis externa were determined by thin layer chromatography and were subsequently used to produce a standardised synthetic cerumen (SCC). SCC was filled into capillary tubes, all of which were loaded with six commercially available multipurpose otic medications and two ear cleaners, each mixed with two markers in two experimental setups. These two marker compounds (Oil red O and marbofloxacin) were chosen, since they exhibit different physicochemical drug characteristics by which it is possible to determine and verify the diffusion activity of different types of liquids (i.e. the otic preparations). A synthetic cerumen described in the literature (JSL) was also used for comparison as its lipid composition was different to SCC. The diffusion activities of the otic preparations through both types of synthetic cerumen were studied over 24 hours. A second in-vitro experiment determined both the ceruminolytic activity and impregnation effect of the otic preparations by comparing the weight loss or weight gain after repeated incubation of JSL.
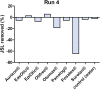
Results: Canine cerumen is mainly composed of triglycerides, sterol esters, fatty acid esters and squalene. The diffusion experiments showed a high diffusion efficacy along with a high impregnation effect for one test product. All the other products exhibited a lower diffusion activity with a mild to moderate impregnation effect. A mild ceruminolytic activity was observed for the two ear cleaners but not for any of the otic medications.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrates that there are significant differences in the diffusion characteristics and ceruminolytic properties of the eight tested otic preparations.
Figures
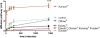



Similar articles
-
In vitro investigation of ceruminolytic activity of various otic cleansers for veterinary use.Vet Dermatol. 2006 Apr;17(2):121-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3164.2006.00504.x. Vet Dermatol. 2006. PMID: 16515654
-
Ceruminolytic agents.J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 1998 Jul-Aug;34(4):273-4. doi: 10.5326/15473317-34-4-273. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 1998. PMID: 9657157 No abstract available.
-
Study to assess in vitro antimicrobial activity of nine ear cleaners against 50 Malassezia pachydermatis isolates.Vet Dermatol. 2013 Jun;24(3):362-6, e80-1. doi: 10.1111/vde.12024. Epub 2013 Apr 2. Vet Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23551137
-
Topical ear treatment - options, indications and limitations of current therapy.J Small Anim Pract. 2016 Dec;57(12):668-678. doi: 10.1111/jsap.12583. Epub 2016 Oct 16. J Small Anim Pract. 2016. PMID: 27747880 Review.
-
Otomycosis due to Aspergillus spp. in a dog: case report and literature review.Vet Dermatol. 2010 Dec;21(6):613-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3164.2010.00903.x. Vet Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20492628 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into cerumen and application in diagnostics: past, present and future prospective.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2017 Oct 15;27(3):030503. doi: 10.11613/BM.2017.030503. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2017. PMID: 29180914 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Linek M. Otitis externa and media in the dog and cat. Tierarztl Prax Ausg K Kleintiere Heimtiere. 2011;39:451–463. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

