Human placental microRNAs and preeclampsia
- PMID: 23575145
- PMCID: PMC4013914
- DOI: 10.1095/biolreprod.113.107805
Human placental microRNAs and preeclampsia
Abstract
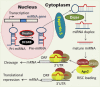
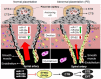
MicroRNAs are a class of noncoding small RNAs that regulate the expression of nearly 30% of all the human genes and participate in all fundamental cell processes. Genome-wide analysis has revealed that human placenta expresses more than 600 miRNA species, including placenta-specific ones with high levels of expression. Comparative analysis also has revealed many differentially expressed miRNAs with either high or low levels of expression in human placentas from normal versus preeclamptic pregnancies, indicating an important role of miRNAs in normal and pathological placental physiology. Although limited information is currently available as to how miRNA regulates human placental development and function, there are studies suggesting that preeclampsia-associated differentially expressed miRNAs possess critical roles in regulating placental development and function via targeting specific genes with diverse known functions. Herein we summarize the current findings regarding the expression of placental miRNAs and their function, especially in the trophoblast cells. We have recently found that the angiogenesis-associated miR-17-family miRNAs are upregulated in preeclamptic compared with normotensive placentas and they target the ephrin-B2/Eph receptor B4 (EPHB4) system. Because ephrin-B2 and EPHB4 has been previously shown to play a crucial role in trophoblast invasion into maternal spiral artery and vascular patterning during early human placental development, the miR-17-ephrin-B2/EPHB4 pathway seems to be a novel miRNA pathway for regulating normal and aberrant placental development during preeclampsia.
Keywords: microRNA; placenta; placentation; preeclampsia; pregnancy.
Figures
References
-
- Redman CW, Sargent IL. Latest advances in understanding preeclampsia. Science 2005; 308: 1592 1594. - PubMed
-
- Roberts JM, Cooper DW. Pathogenesis and genetics of pre-eclampsia. Lancet 2001; 357: 53 56. - PubMed
-
- Sitras V, Paulssen RH, Gronaas H, Leirvik J, Hanssen TA, Vartun A, Acharya G. Differential placental gene expression in severe preeclampsia. Placenta 2009; 30: 424 433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

