FBXW7α attenuates inflammatory signalling by downregulating C/EBPδ and its target gene Tlr4
- PMID: 23575666
- PMCID: PMC3625980
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2677
FBXW7α attenuates inflammatory signalling by downregulating C/EBPδ and its target gene Tlr4
Abstract
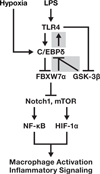
Toll-like receptor 4 (Tlr4) has a pivotal role in innate immune responses, and the transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta (C/EBPδ, Cebpd) is a Tlr4-induced gene. Here we identify a positive feedback loop in which C/EBPδ activates Tlr4 gene expression in macrophages and tumour cells. In addition, we discovered a negative feedback loop whereby the tumour suppressor FBXW7α (FBW7, Cdc4), whose gene expression is inhibited by C/EBPδ, targets C/EBPδ for degradation when C/EBPδ is phosphorylated by GSK-3β. Consequently, FBXW7α suppresses Tlr4 expression and responses to the ligand lipopolysaccharide. FBXW7α depletion alone is sufficient to augment pro-inflammatory signalling in vivo. Moreover, as inflammatory pathways are known to modulate tumour biology, Cebpd null mammary tumours, which have reduced metastatic potential, show altered expression of inflammation-associated genes. Together, these findings reveal a role for C/EBPδ upstream of Tlr4 signalling and uncover a function for FBXW7α as an attenuator of inflammatory signalling.
Figures






References
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity. 2011;34:637–650. - PubMed
-
- Lin Q, Li M, Fang D, Fang J, Su SB. The essential roles of Toll-like receptor signaling pathways in sterile inflammatory diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011;11:1422–1432. - PubMed
-
- Huang B, et al. Toll-like receptors on tumor cells facilitate evasion of immune surveillance. Cancer Res. 2005;65:5009–5014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

