Evaluating the role of neuronal nitric oxide synthase-containing striatal interneurons in methamphetamine-induced dopamine neurotoxicity
- PMID: 23575992
- PMCID: PMC3692605
- DOI: 10.1007/s12640-013-9391-6
Evaluating the role of neuronal nitric oxide synthase-containing striatal interneurons in methamphetamine-induced dopamine neurotoxicity
Abstract
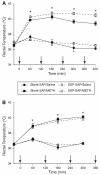
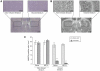
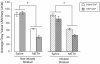
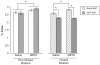
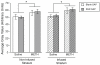
Production of nitric oxide (NO) has been implicated in methamphetamine (METH)-induced dopamine (DA) neurotoxicity. The source of this NO has not been clearly delineated, but recent evidence suggests that it arises from activation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), which is selectively expressed in a subpopulation of striatal interneurons. Our objective was to determine whether inhibiting activation of nNOS-containing interneurons in the striatum blocks METH-induced neurotoxicity. These interneurons selectively express the neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptor, which is activated by substance P. One particular toxin, a conjugate of substance P to the ribosome-inactivating protein saporin (SSP-SAP), selectively destroys neurons expressing the NK-1 receptor. Thus, we examined the extent to which depletion of the nNOS-containing interneurons alters production of NO and attenuates METH-induced neurotoxicity. The SSP-SAP lesions resulted in significant loss of nNOS-containing interneurons throughout striatum. Surprisingly, this marked deletion did not confer resistance to METH-induced DA neurotoxicity, even in areas devoid of nNOS-positive cells. Furthermore, these lesions did not attenuate NO production, even in areas lacking nNOS. These data suggest that nNOS-containing interneurons either are not necessary for METH-induced DA neurotoxicity or produce NO that can diffuse extensively through striatal tissue and thereby still mediate neurotoxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Abekawa T, Ohmori T, Koyama T. Effects of nitric oxide synthesis inhibition on methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic and serotonergic neurotoxicity in the rat brain. J Neural Transm. 1996;103(6):671–680. - PubMed
-
- Bergstrom BP, Garris PA. “Passive stabilization” of striatal extracellular dopamine across the lesion spectrum encompassing the presymptomatic phase of Parkinson’s disease: a voltammetric study in the 6-OHDA-lesioned rat. J Neurochem. 2003;87(5):1224–1236. - PubMed
-
- Bittner SE, Wagner GC, Aigner TG, Seiden LS. Effects of a high-dose treatment of methamphetamine on caudate dopamine and anorexia in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1981;14(4):481–486. - PubMed
-
- Bowyer JF, Davies DL, Schmued L, Broening HW, Newport GD, Slikker W, Jr, Holson RR. Further studies of the role of hyperthermia in methamphetamine neurotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;268(3):1571–1580. - PubMed
-
- Brown JM, Quinton MS, Yamamoto BK. Methamphetamine-induced inhibition of mitochondrial complex II: roles of glutamate and peroxynitrite. J Neurochem. 2005;95(2):429–436. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03379.x. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

