Expression of glycosaminoglycan epitopes during zebrafish skeletogenesis
- PMID: 23576310
- PMCID: PMC3698701
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.23970
Expression of glycosaminoglycan epitopes during zebrafish skeletogenesis
Abstract
Background: The zebrafish is an important developmental model. Surprisingly, there are few studies that describe the glycosaminoglycan composition of its extracellular matrix during skeletogenesis. Glycosaminoglycans on proteoglycans contribute to the material properties of musculo skeletal connective tissues, and are important in regulating signalling events during morphogenesis. Sulfation motifs within the chain structure of glycosaminoglycans on cell-associated and extracellular matrix proteoglycans allow them to bind and regulate the sequestration/presentation of bioactive signalling molecules important in musculo-skeletal development.
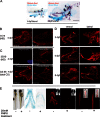
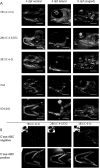
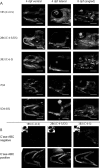
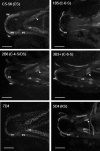
Results: We describe the spatio-temporal expression of different glycosaminoglycan moieties during zebrafish skeletogenesis with antibodies recognising (1) native sulfation motifs within chondroitin and keratan sulfate chains, and (2) enzyme-generated neoepitope sequences within the chain structure of chondroitin sulfate (i.e., 0-, 4-, and 6-sulfated isoforms) and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans. We show that all the glycosaminoglycan moieties investigated are expressed within the developing skeletal tissues of larval zebrafish. However, subtle changes in their patterns of spatio-temporal expression over the period examined suggest that their expression is tightly and dynamically controlled during development.
Conclusions: The subtle differences observed in the domains of expression between different glycosaminoglycan moieties suggest differences in their functional roles during establishment of the primitive analogues of the skeleton.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Adams SL, Cohen AJ, Lassová L. Integration of signaling pathways regulating chondrocyte differentiation during endochondral bone formation. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:635–641. - PubMed
-
- Apschner A, Schulte-Merker S, Witten PE. Not all bones are created equal: using zebrafish and other teleost species in osteogenesis research. Methods Cell Biol. 2011;105:239–255. - PubMed
-
- Avnur Z, Geiger B. Immunocytochemical localization of native chondroitin-sulfate in tissues and cultured cells using specific monoclonal antibody. Cell. 1984;38:811–822. - PubMed
-
- Bayliss MT, Osborne D, Woodhouse S, Davidson C. Sulfation of chondroitin sulfate in human articular cartilage. The effect of age, topographical position, and zone of cartilage on tissue composition. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:15892–900. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

